Ancient Rome remains shrouded in mystery since it is difficult to determine its exact founding date. Historians believe that Rome was founded by Romulus, an exiled prince from the Troy region, in 753 BC. This date is still up for debate because there is no mention of the founding of Rome in any of the historical documents of that time. It is, however, believed that a settlement in the area existed from much earlier times.
Archaeological evidence suggests that the Palatine Hill area of Rome began to be inhabited as early as 1000 BC. This period saw a number of small villages springing up in the region and artisans and merchants settling in the area. The development of the region continued to grow until Rome became a major center of the Mediterranean.
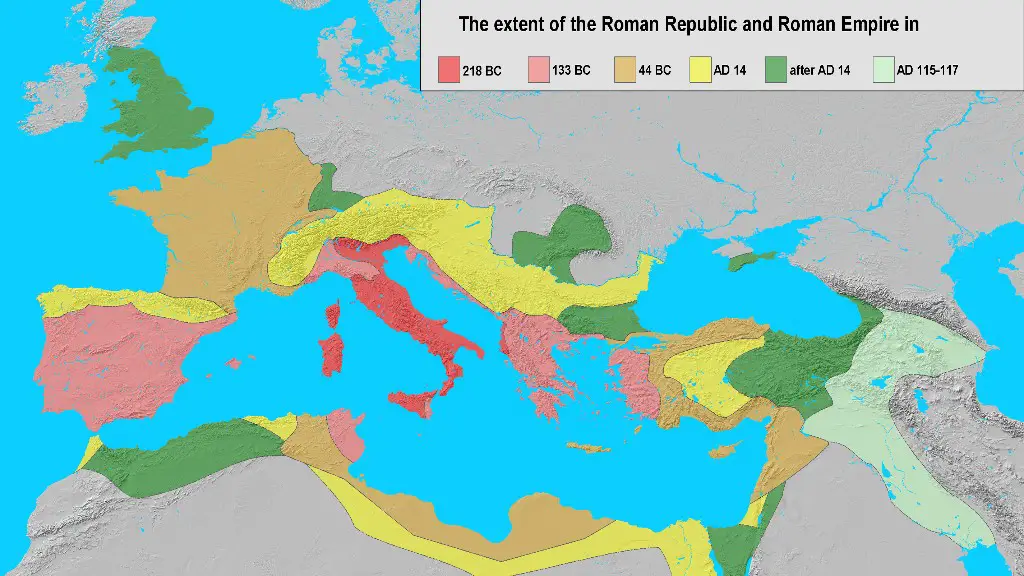
Rome’s ascension to power was marked by a number of political, military and economic events that began to shape the city in the period of the 500s BC. The city was gradually becoming more influential, and by c. 477 BC, it was an established city-state, dominating much of Italy. It was during this period that Rome became a Republic and developed the beginnings of its formidable constitution.
At this stage, Rome was well on its way to becoming one of the most powerful cities in the Mediterranean. Rome was able to expand its influence because of its strong military, which won a number of wars against the surrounding enemy states. This allowed Rome to conquer the lands of its enemies and bring them under the control of the Republic.
As Rome’s influence continued to spread, a certain amount of Macedonian influence began to be apparent in the city. Rome also began to assimilate aspects of Greek culture and language, developing a rich particular city culture, which was to become the foundation of what would become the famous Roman Empire.
The Roman Republic gradually shifted into the Roman Empire in the late 1st century BC and by 27 BC, the empire was firmly established. Under the rule of Augustus, Rome rapidly grew in power, taking control of the entire Mediterranean and beyond. Rome was able to unify and centralize much of the Western world in the 1st century AD.
In conclusion, while it is impossible to determine the exact founding of Rome, historians do place it around 753 BC. From there, the city-state grew in power over a period of centuries, eventually becoming one of the most powerful entities in the Mediterranean and a force that shaped the history of the world for centuries.
Relationships with the Surrounding Nations
Rome’s expansionist policies during its early years had a significant impact on its relationship with the surrounding areas. During the Republic, diplomatic relations between Rome and the neighbouring cities and states were based on treaties and agreements. Rome also established strong trade relationships as it sought to expand its influence in the region by bringing in new forms of income and resources. While Rome was able to bring much of the region under its control, its neighbours also became important allies, helping to protect Rome from attack.
Many of the cities surrounding Rome were allied with the Republic, and when the Empire was established, Rome was able to extend its control to many other states. This had some significant implications for regional stability, creating a web of alliances and setting up a structure that led to a strong regional presence.
The Republic was also able to establish itself as a leader within the region, setting up a number of reforms that led to increased trade and increased stability. This meant that Rome was able to expand its reach to many different parts of the world, and eventually became an important regional power.
The expansion of Rome’s reach and influence led to the emergence of many new cultures in the region, which were heavily influenced by the Roman way of life. Rome had a significant influence on the spread of Christianity, which was brought to the region by Roman missionaries, and was eventually accepted as the official religion of the Empire.
The Roman Economy
Rome’s rise to power coincided with the emergence of a strong and vibrant economy, which helped to support the city’s political and military ambitions. The Roman economy was heavily dependent on agriculture, with the surrounding countryside providing resources to the city. Rome also took advantage of its connection to the Mediterranean to trade with other cities and states, fostering a number of important economic relationships.
Rome also developed sophisticated systems of banking, taxation and coinage that provided an effective way for the city to raise funds for its projects. This allowed Rome to finance its military campaigns and extend its influence, as well as ensuring economic stability for the citizens.
The economy was also bolstered by the construction of a series of roads and bridges, which connected Rome to the surrounding areas and enabled increased trade and cultural interchange. This allowed Rome to become a hub of commerce, which helped further to increase its wealth and power.
Rome also developed a number of new technologies, which enabled them to continue to expand both their military might and their economic power. This included a number of engineering developments, such as aqueducts, which allowed them to bring water to the city and make Rome a major center of trade and commerce.
Agriculture and Development
Rome’s development was largely dependant on agriculture, which provided the city with essential resources such as food and materials. As the Roman Empire expanded, it developed a number of techniques to aid agricultural production and increase crop yields. This included a network of irrigation systems, which helped to bring water to areas that were difficult to reach by a traditional canal system.
Rome also developed a number of techniques to prepare soil for planting, and to help control weeds and pests. This allowed them to make better use of the land, and to increase production for the city and its population. This was a major factor in the rise of the Roman Empire, as it provided the city with a reliable and steady supply of resources and allowed them to increase their wealth and power.
At the same time, Rome increased its trade links with other cities, transporting goods across the Mediterranean and to the furthest reaches of the Empire. This allowed Rome to become a hub of commerce and increased the wealth of the city. Rome also set up colonies in the provinces, which allowed them to maintain control of far-flung areas, as well as enabling them to increase the production of their goods.
Rome was also a major center for industry and manufacturing, and this was an important part of their economic success. By focusing on industrial production, Rome was able to manufacture goods quickly and efficiently, providing an essential resource to the city and its citizens. This helped to finance Roman military projects, allowing them to expand further and further abroad.
Cultural Expression
One of the most important aspects of Rome’s success was its ability to absorb and assimilate other cultures into its way of life. Rome was able to incorporate a number of different customs, beliefs and faiths into its culture, creating a vibrant and diverse society. This contributed to the development of a unique Roman culture, which was marked by innovation and creativity. Rome also allowed a number of different forms of self-expression, such as literature, sculpture and architecture, which aided in the development of a unique and powerful culture.
The Roman Empire was also an important period of technological innovation, with advances in engineering and construction that allowed the Romans to create an extensive network of roads and bridges. This allowed them to increase trade, reduce travel times and foster greater levels of communication. Rome also made advances in medicine, with public health and hygiene becoming more important in the city. This enabled the Romans to develop a number of remedies and treatments, which helped them to maintain their health and wellbeing.
Rome also had a strong educational system, in which a number of different educational ideals were taught. This included rhetoric, philosophy and mathematics, as well as a number of other disciplines that helped to shape the Roman culture. Rome was also able to preserve its culture overtime, as it was able to create an effective system of libraries and archives, which helped to secure the city’s knowledge and wisdom for future generations.
The culture of Rome was one of the key factors in its success, as it allowed the city to draw upon a variety of different influences and create a unique identity. This allowed the city to become a hub of art, science, and commerce, which allowed it to become one of the most powerful cities in the Mediterranean.