Ancient Rome And Its Cities
The ancient Roman Empire was one of the most powerful civilizations in history, spanning almost 700 years. As Rome developed, cities became more important, acting as vital centers of trade, industry, and culture. So, what were these cities?
Most scholars agree that there were three main cities in ancient Rome: Rome, Capua, and Ostia. While Rome was the seat of the government and the Cicero, the capital city of the Republic, the other cities played an important role too.
Capua was the largest city of the two, with a major military base and estate. This city was considered the gateway from the Samnite hill country to the lowlands of Campania. It was also believed to be the first example of a Roman colony.
Ostia was an important port city. Located at the mouth of the Tiber River, it provided the Roman Empire with trade goods from all over the Mediterranean. It was also a major base for the fleet, allowing them to provide defense against pirate attacks.
The other cities weren’t nearly as important as the three mentioned above, but played a vital role in the development of ancient Rome. Among these other cities were: Aquileia, Ariminum, Arretium, Aesernia, Beneventum, Brixia, Cales, Neapolis, Portus, Ostia, Saturnia, and Placentia.
Each of these cities specialized in a specific product or service, such as pottery, arms manufacturing, and grain production. This allowed them to capitalize on their strengths and specialize in their own particular product. This specialization allowed them to become the most prosperous cities of their time.
Ancient Rome also had a few other cities, or “municipia”, that were built for special reasons. One of the most important of these was Ostia, which was built to protect the Tiber River from being raided by pirates. Other cities included Tibur, Praeneste, and Aeclanum, which were built for the purpose of providing trade opportunities.
In addition to cities, ancient Rome also had a vast network of roads, the most famous of which was the Appian Way. This road connected the capital city of Rome to the rest of the empire, becoming a veritable superhighway of its time.
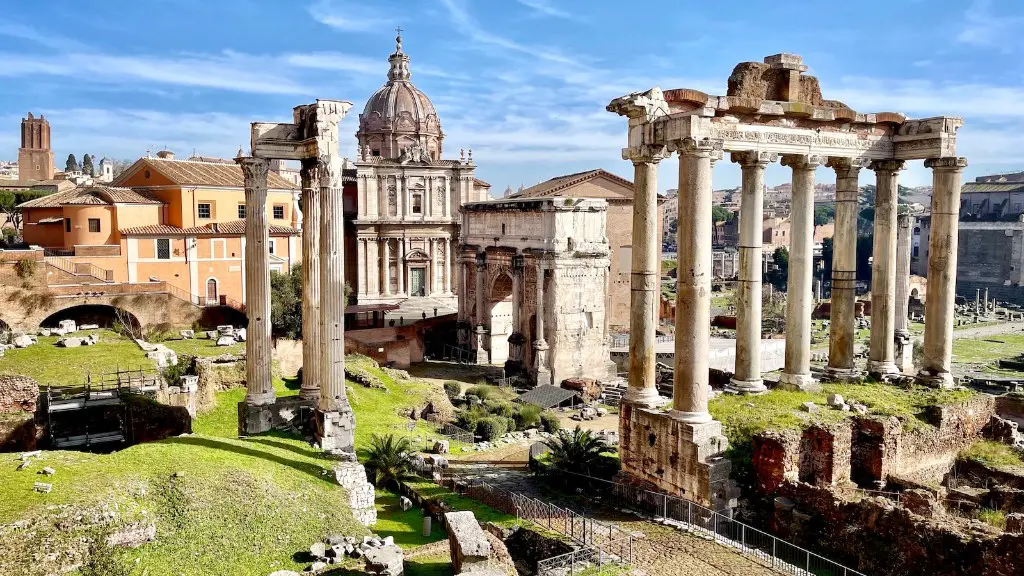
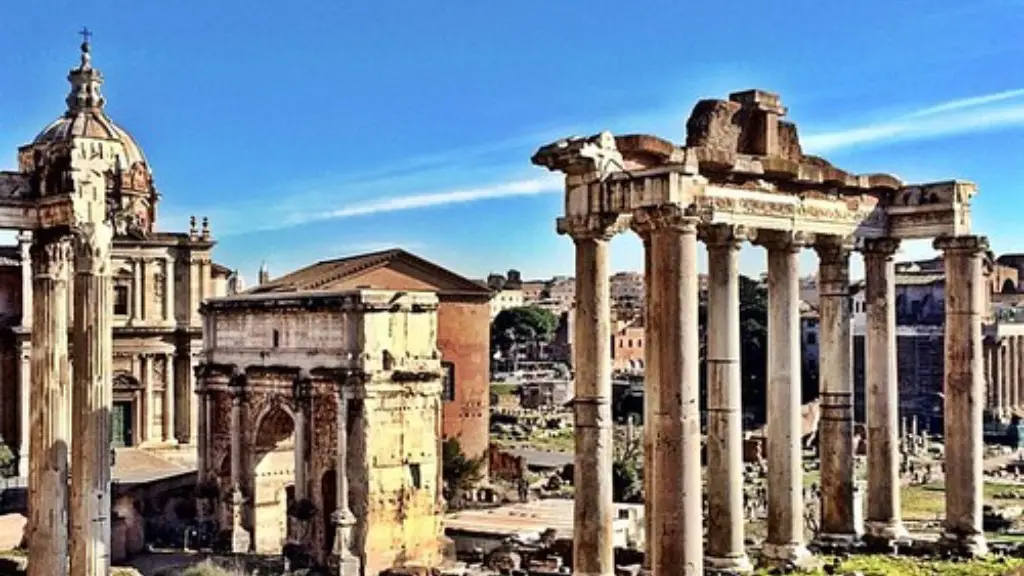
Today, many of these cities still exist and can be visited. However, it’s important to remember that they are ruins, and only hint at the glory that once was ancient Rome.
Ancient Roman Economy
An important factor in the development of ancient Rome was its economy. The Roman economy was based on the free market and supported commerce and trade, which allowed it to flourish. This economy was based on three main sources: farming, trade, and manufacturing.
Farming was the main source of food, and the most common form of agricultural production was cattle. Other forms of farming included vineyards, orchards, vegetable gardens, and grain production. This variety provided Rome with a healthy, balanced diet of both animal and plant-based foods.
Trade was an important source of wealth for Roman cities. Goods from all over the Mediterranean and beyond ended up in Roman markets. These goods included: grain, pottery, wine, olive oil, and jewelry.
Manufacturing was a major component of the Roman economy as well. Raw materials like iron and marble, as well as goods like pottery, clothing, and furniture, were produced in factories all over the Roman Empire. This allowed Rome to remain a major player in the international market.
The Roman economy was further supported by slave labor, which was prevalent throughout the empire. This labor allowed Rome to increase its production significantly and serve as a major trading partner with the rest of the Mediterranean.
The strength of the Roman economy was demonstrated by their ability to maintain their currency, even during economic downturns. This allowed for continued development and made Rome an attractive market for goods from all over the world.
Ancient Roman Religion
Religion was an integral part of the lives of ancient Romans. They believed in gods and goddesses, as well as a wide range of rituals and ceremonies. These ceremonies celebrated the gods and goddesses and provided a way to bring balance to the natural order. This belief system was echoed in the architecture of Rome, which featured temples, shrines, and altars dedicated to the gods and goddesses.
The most important god for the Romans was Jupiter, the king of the gods. He was the protector of the state and was represented by the wolf. Along with Jupiter, there were other gods and goddesses, including Juno, the goddess of marriage and family; Ceres, the goddess of fertility; Mars, the god of war. Worship of these gods was widespread throughout the empire and featured both public and private ceremonies.
The religion was also influential in politics, as it provided the basis for the divine right of the Emperor. This idea was advanced by Julius Caesar, who declared himself the divine ruler of Rome. This was further cemented with the creation of the worship of the Julio-Claudian dynasty. This belief system remained a powerful influence in Roman society until the end of their civilization.
Architecture Of Ancient Rome
The architecture of Rome was a reflection of the empire’s power and influence. The most famous example of this was the Colosseum, which was built during the reign of Vespasian as a gift to the Roman people. This structure featured a large oval seating area and was used for gladiator fights and public entertainment. Other famous examples of Roman architecture include the Pantheon, the Baths of Caracalla, and the Circus Maximus.
Public buildings were also an important part of the civic landscape of Rome. These included the Forum, which served as a public center for the city. other important public buildings were the temples and shrines to the gods, which served as major religious centers. Libraries, theatres, marketplaces, and aqueducts were also common.
One of the most impressive examples of Roman architecture were the bridges that were built over the Tiber River. These bridges allowed the people to cross the river with ease and provided a strong link between the two sides of the city. Not to be forgotten are the walls and fortifications that provided Rome with protection.
The architecture of Rome provides a tangible example of the power, grandeur, and influence of the ancient Roman Empire. Even today, we can still marvel at the skill of the architects and engineers who built these structures.
The Legacy Of Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome is regarded as one of the great civilizations of history, and its legacy is still felt today. Its art, literature, architecture, and laws have all been adopted by modern society, and its influence can be seen in many aspects of our daily lives.
The Latin language is the foundation of many modern Romance languages, such as Italian, Spanish, French, and Portuguese. Roman law has been adopted by many modern countries, and its contribution to the development of concepts such as citizenship, property, and justice has been invaluable. Its architecture has been duplicated in Russia, Spain, and the United States.
The legacy of Rome also extends to its literature and art. Its literature profoundly shaped the Western world and is still studied today. Its art, with its emphasis on the human form, provided a model that has been adopted by artists in the centuries since.
The legacy of ancient Rome is also evident in its technology and engineering, such as its use of cement, aqueducts, and roads. These advances have allowed modern civilizations to build and maintain complex infrastructure and transportation systems.
The legacy of ancient Rome is still visible today, and its influence is profound. It is a testament to the power and tenacity of the Roman Empire, and its legacy will be felt for centuries to come.