Houses in ancient Rome have been the subject of much study, curiosity and admiration. The advancements made in the Roman architectural style have been a model for many centuries. Even today, many of our modern houses and buildings share some features with their ancient predecessors.
Some of the factors of construction of a house in ancient Rome included the weather and the materials available. Ancient Rome is situated in a warm and temperate climate, and this meant that the use of materials such as mortar and mud-related substances were primary. In addition to this, the locally available soft rocks such as limestone, chalk and tufa were used to make walls and was often combined with reed, twigs and clay for flooring.
Furthermore, brick was also a popular choice of material in terms of building houses in ancient Rome, especially when the objective was to erect large houses or buildings. Bricks were made using a combination of clay, sand and straw. A kiln was also used for heating them to a suitable temperature before using them for construction.
Wood was also used in house construction and typical examples include doors and windows. Other materials used in the building of a house in ancient Rome included marble, travertine and stucco.
The techniques used by the ancients to build houses were also very efficient. Construction would start with the digging and preparation of the foundation trench. The trench would be filled with crushed tile, rocks and cement and topped with a layer of soil which acted as a cushion. After that, walls were made and floors were also constructed. Plastering was used to cover interior and exterior walls. Windows and doors were also installed along with their fixtures.
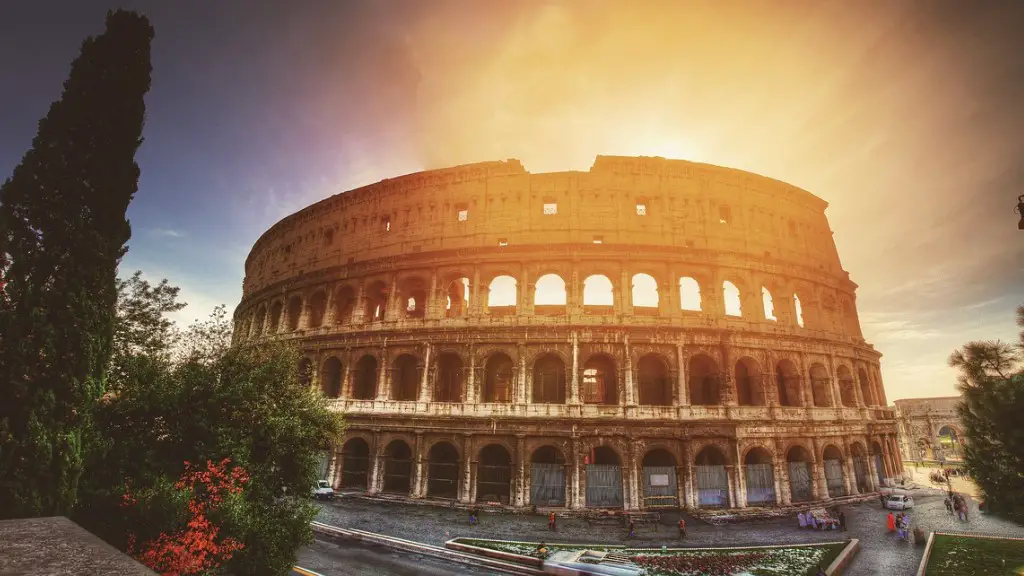
Ancient Rome was also known for its amazing engineering capabilities, and one of the best examples of this is the construction of the Colosseum, which was built by the Emperor Vespasian in 79 AD. The Colosseum was built with a combination of concrete, stone, stucco, mortar and bricks. It is a testimony of the power and talent of the engineers of ancient Rome.
Societal Influences
The ancient Roman society was composed of two classes of people; the patricians and the plebians. The patricians were the upper-class citizens and the plebians the lower-class citizens. This influenced the way houses were built in ancient Rome as, depending on the class, certain materials were used to signify wealth and power, such as marble, travertine and other expensive ones. Wealthier households also had access to higher-quality materials.
The designs of ancient roman houses were also influenced by the social status of its occupants. Patricians were known to live in villas, which were large and luxurious homes that often included features such as paved floors, tiled roofs, walls decorated with paintings and statues, mosaics, interior courtyards and colonnaded walkways. This was in contrast to the houses of the plebians which were much smaller and more basic in their design.
It is important to note that the designs of both patrician and plebian houses were influenced by the class society of Ancient Rome.
Urban Planning & Development
Ancient Roman houses used a grid-like design system. This design was seen in the layout of the city, with the main streets divided by narrow alleys and narrower side streets. Urban planning was very important in Ancient Rome and the development of houses followed very specific rules for their layout and construction. This included the division of space into two or even three storeys, with levels dedicated to either rental or own-use.
Furthermore, the grid-like design of the city and the division between main and side streets had a direct influence on the physical layout of the houses themselves. For example, some houses featured a front door that opened directly onto the main streets and other houses featured a courtyard that overlooked the alleyways.
The rules of urban planning also dictated the use of materials. For example, while most ancient Roman houses were made of mortars and mud, the wealthier classes had access to better-quality materials, such as marble and travertine.
Interior Design
Despite their differences in design and materials, the interior of ancient Roman houses shared certain features. These included plastered walls, tiled roofs and cement or ivy-covered walls. The walls were usually painted in various colours, and this was a way to express the personality of its occupants. The interior of a house was also a reflection of its owner’s wealth, and wealthier households had access to more luxurious features, such as mosaics and statues.
One of the most important features of a house was the hypocaust, which was used to heat the interior of the house. The hypocaust was a system of raised tile floors and walls heated by hot air beneath the floor. The hypocaust was used in the homes of both patricians and plebians and was seen as a luxurious feature.
Another important feature of a house in ancient Rome was the domus, which was the residence of the Roman family. The domus was usually divided into two parts, the atrium and the tablinum. The atrium was the main living area and featured an open courtyard. The tablinum was used for dining and featured a compluvium, which was a small pool that helped to bring in natural daylight.
Architectural Decoration & Functionality
The most impressive feature of many ancient Roman houses was the use of architectural decoration. This included the use of friezes, columns and other features to add aesthetic value to a building. The use of mosaic tile was also popular and helped to make a house look more luxurious and impressive. The use of these features was a way to showcase the wealth and status of its occupants.
Another important functional feature of Roman houses was the use of gardens and balconies. These features were used to bring in natural light and air into the house, while also providing additional space for entertaining and relaxation. The gardens were often used to grow food and herbs, and the balconies were used to enjoy the beautiful views of the surrounding city.
The houses in ancient Rome were also built to be durable and long-lasting. The use of mortar and mud-related materials was key to creating strong foundations and walls that were resistant to the weather and earthquakes. This ensured that ancient Roman houses were able to stand the test of time.
Environmental Sustainability
Roman houses were also designed to be highly energy efficient and some of their innovations were ahead of their time. For instance, the hypocaust was a system to conserve energy and heat the interior of the house. Windows and balconies also helped to bring in natural light and air, reducing the need for artificial lighting and ventilation.
The ancient Romans also had specific rules and regulations in place to ensure that their houses were built sustainably. This included the use of harvested wood, the use of stone and clay, and the prohibition of the over-extraction of resources. Similarly, they had laws in place to prevent the pollution of the environment, such as the prohibition of the burning of wood and other materials.
The sustainable practices of the Ancient Romans are a testament to their engineering capabilities and their knowledge of the environment. These practices were ahead of their time, and are still relevant today.
Legacy
The houses of ancient Rome continue to influence our modern houses and buildings. Many of the techniques and materials that were used by the Ancient Romans are still in use today. Architects and engineers continue to be inspired by the ingenuity of their predecessors, and it is clear that the legacy of ancient Roman houses will continue to influence our modern architectural styles.
The houses of ancient Rome are a testament to the engineering capabilities of the ancients and the ingenuity of their architects and engineers. The architectural styles and materials used in their construction have stood the test of time and continue to be an inspiration to modern architects and engineers.