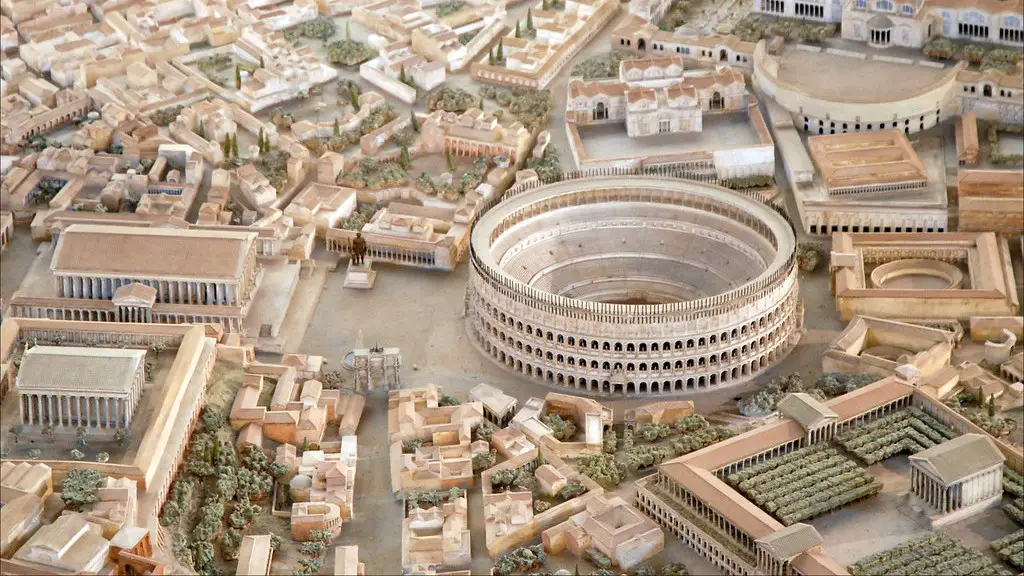
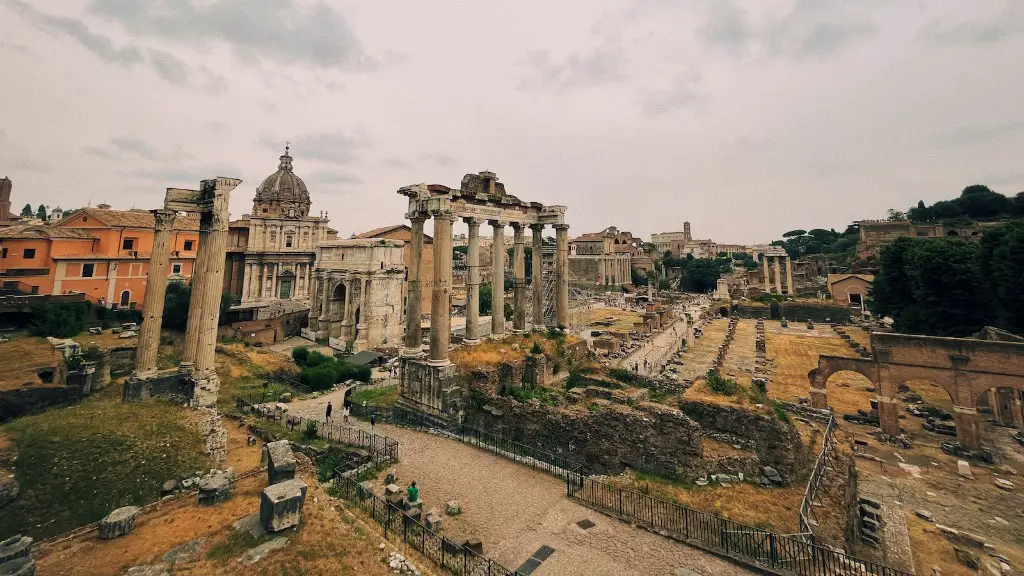
Over the centuries, there have been many different ways of measuring temperature. The first recorded instance of temperature measurement dates back to ancient Rome. The ancient Romans used a system of measurement called “degrees”. Degrees were based on the temperature at which water boiled or froze. The zero point was arbitrary, but by convention, it was set at the average temperature of the human body, which is about 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit.
The average temperature in ancient Rome was 23.6 degrees celsius.
Was it warm in ancient Rome?
Ancient Rome was located on the Mediterranean Sea and had warm summers and mild winters. This type of climate is referred to as a Mediterranean climate. At first, the Roman kingdom was just located near where the modern city of Rome is. But as the kingdom grew, it eventually included all of the land around the Mediterranean Sea.
The Roman climate was characterized by cool summers and mild, rainy winters. At the same time, there were a number of drastic winters, including the complete freezing of the Tiber in 398 BC, 396 BC, 271 BC, and 177 BC.
Why was it hotter in Roman times
The historical warming of the Mediterranean during the Roman Empire was likely due to intense solar activity during that time period. This is in contrast to the modern threat of greenhouse gases, which are a much greater threat to the planet today.
The ancient Roman plumbing system was a remarkable feat of engineering, providing fresh water to urbanites from hundreds of kilometers away. Wealthy Romans had access to hot and cold running water, as well as a sewage system that quickly removed waste. This system was a major contributor to the success of the Roman Empire, and its legacy can still be seen in modern plumbing systems.
How hot were Roman baths?
A hot spring is a natural spring where the water is heated by geothermal energy. The water temperature can be between 69 and 96 °C (1562 and 2048 °F). The heated water rises along fissures and faults in the limestone, until it bubbles up from the ground into the baths.
The wealthiest people in ancient Rome had access to luxuries that weren’t available to everyone. One of these luxuries was underfloor heating, known as hypocaust. This heating system, more common in public baths, used a furnace to force heat into a series of hollow chambers between the ground and the floor, and up pipes in the wall, heating the rooms. The wealthy could enjoy this luxury while the rest of the population had to make do with less comfortable heating options.
Was ancient Rome hot or cold?
The climate in Rome is quite mild, with average temperatures of 30˚C during the day, and 18˚C at night. However, it is important to note that the Mediterranean region is characterised by dry and hot summers, and cold and humid winters. As a result, visitors should be prepared for extreme weather conditions when travelling to Rome.
The Roman climate was characterized by cool summers and mild, rainy winters. At the same time, there were a number of severe winters, including the complete freezing of the Tiber in 398 BC, 396 BC, 271 BC and 177 BC.
Did it ever snow in Rome
Snow is a rare occurrence in Rome. In the last twenty years, it has only snowed seven times, and only a handful of those times has brought more than a light dusting. The snowfall of 1956 in Rome is historical as it brought to Rome a proper blanket of snow that covered the city for several days.
The Neoproterozoic is a geologic period that lasted from 1 billion to 541 million years ago. It is characterized by extreme heat, with temperatures reaching up to 58 degrees Celsius. This was caused by a combination of factors, including high carbon dioxide levels, strong sunlight, and a lack of an ozone layer. This period was also marked by frequent mass extinctions, as well as the rise of complex life forms.
How hot was Earth during the dinosaurs?
This research shows that dinosaurs in the northern hemisphere lived in extreme heat. The average summer temperatures were around 27 degrees. There were days when the temperature crept above 40 degrees. However, the winters were mild and wet. This research was conducted by Nicolas Thibault.
The Roman’s were quite ingenious when it came to keeping their homes cool during summer months. By pumping cold water from aqueducts through the walls of their homes, they were able to create a refreshing and cool environment to escape the heat. This was a luxury that was only afforded to the elite, but it was a clever way to beat the summer heat.
How did the Romans wipe their bottoms
The tersorium was a popular cleaning tool among the ancient Romans. It was a sea sponge attached to a stick, which was used to wipe the body clean. The gutter supplied clean flowing water to dip the sponges in, and the tersorium was a soft, gentle way to clean oneself.
It is interesting to note that the practice of bathing every nine days was introduced to Italy from Greece. This would suggest that the Greeks were more cleanly than the Romans. However, it is also worth noting that the Romans were not completely dirty. They would wash their arms and legs every day, which would get dirty from working.
How was hygiene in Roman times?
The poor in Rome did not have access to the same hygiene facilities as the wealthy. This often led to health problems, as the poor were more likely to be exposed to diseases. The government should provide more access to hygiene facilities for the poor to help improve their health.
According to contemporary reports, the toilets and public baths in Rome were heavy with the smell of excrement, urine and disease. This must have been a very unpleasant experience for the people who used them. However, it is also clear that these facilities were used extensively by the population.
This provides us with a vivid picture of daily life in Rome, one that reveals both the risks and the delights of that ancient society. On the one hand, it was clearly a very dirty place, with widespread disease and poor sanitation. On the other hand, the people of Rome seem to have been quite tolerant of these conditions, and they continued to use these facilities despite the unpleasant smells.
This paradoxical situation highlights the importance of historical context in understanding the past. Without knowing the full context, it would be easy tojudge the people of Rome harshly for their poor sanitation. However, when we understand the conditions under which they lived, we can see that they were actually quite resourceful in dealing with the challenges of their environment.
Warp Up
There is no definitive answer to this question as the temperature in ancient Rome would have varied depending on the time of year and the location within the city. However, average temperatures in Rome are generally quite mild, with average highs in the summer months (July and August) ranging from 24-26 degrees Celsius (75-79 degrees Fahrenheit) and average lows in the winter months (December and January) ranging from 4-6 degrees Celsius (39-43 degrees Fahrenheit).
There is no definitive answer to this question as there are no detailed records of temperature in ancient Rome. However, based on the climate of Rome today and other factors such as the city’s location and elevation, it is estimated that the average temperature in ancient Rome was probably around 22 degrees Celsius.