Politics and Economy
At the center of public life in ancient Rome was politics. The Roman Empire was an autocratic monarchy ruled by an emperor, who held absolute power and was responsible for making laws and decisions. The emperor was the head of state and appointed other leaders to administer the provinces of the empire. Citizens could participate in public life by voting for candidates in elections and running for office. The Senate, composed of aristocrats and patricians, was responsible for enacting legislation and administering justice.
As a major superpower, Rome’s politics and economy had a significant impact on the world. Its trade connections stretched from north Africa to east Asia. The city was a major exporter of commodities such as wheat, oil, wine, and other agricultural products. Roman merchants were able to buy products from around the world at lower prices than what they would charge the citizens of Rome. This allowed the Roman economy to thrive and grow, contributing to the wealth and power of the city.
The economy of Rome was controlled by the government. The government would collect taxes from its citizens and use the money to build and maintain infrastructure, fund wars, and finance public works such as aqueducts, roads and temples. The government also controlled prices and set wages and prices for goods and services—which, in theory, ensured a stable and fair economy.
Religion and Society
Religion was a major part of public life in ancient Rome, and the city was home to numerous temples and shrines dedicated to the gods and goddesses of the Roman pantheon. Citizens would visit these religious sites to pray and make offerings to the gods, and animal sacrifices were common practice. This religious faith was central to Roman society, and the gods were seen as being responsible for the city’s successes and failures.
The people of Rome were also a tight-knit community. They shared many social events such as chariot races, theatrical performances, and gladiatorial contests. Roman citizens were also incredibly patriotic and proud of their city, which was the focus of the Roman Empire and its military might.
Apart from the political, economic and religious aspects of public life, there were also underlying cultural values that influenced the daily life of citizens. Ancient Romans placed a high value on honor and glory, and these values were reflected in the way that citizens conducted themselves in public. For example, dressing modestly, speaking in a dignified manner, and being an upstanding member of society were all ways in which Romans sought to present themselves in the public sphere.
Entertainment and Recreation
Entertainment was also an important part of public life for citizens of ancient Rome. People would attend plays, listen to music, go to the public baths, or engage in sports such as chariot racing. Many of these activities occurred in special venues such as amphitheaters or arenas, and a significant portion of the population would gather to watch and participate in these events.
Citizens also took part in recreational activities such as hunting, fishing, and outdoor games. Roman society also afforded citizens the opportunity to relax in the comfort of their own home, which was a major source of entertainment. It was common for citizens to gather in their homes and enjoy food, wine, and conversation. These events often featured games of chance to pass the time.
The entertainment and recreation of ancient Rome was deeply connected to the city’s culture and values. Through the public displays of moral and honorable behavior, citizens sought to present their values to the world and be remembered for their nobler deeds. Entertaining and recreational activities were thus seen as a means to demonstrate one’s honor and glory.
Government Institutions
The government of Ancient Rome also contributed to its public life. The Roman Empire was divided into provinces, each of which was administered by a governor appointed by the emperor. Each province had its own government institutions such as a senate, courts of law, and militia. The emperor was responsible for appointing the officials who would oversee the administration of the provinces.
In addition, the Roman military had a major presence in the city. Soldiers were stationed at the city gates to protect the city from invaders, and centurions also patrolled the streets to maintain order and ensure that citizens obeyed the law. The military was also responsible for ensuring that citizens paid taxes and fulfilled their obligations to the state.
The government of Rome also made provisions for its citizens by distributing food from state-run warehouses and providing public baths. This enabled citizens to enjoy a degree of comfort that was not available to the rest of the population in the Roman Empire.
Culture and the Arts
Culture and the arts were also central to public life in Rome. The city was home to famous painters and sculptors, and their works were highly prized. The city was also home to several renowned theaters, amphitheaters, and arenas, where plays, concerts, and sporting events were performed.
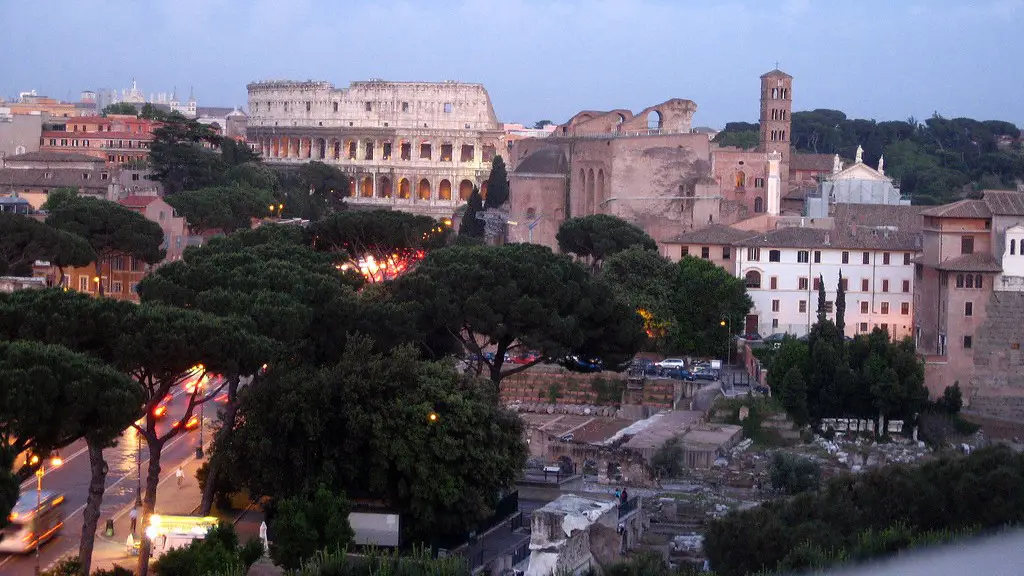
The Roman Empire also contributed to the development of many aspects of Western culture, such as language and architecture. Roman architects constructed some of the most impressive buildings in the world, such as the Colosseum and the Pantheon. The city also had its own unique style of clothing and fashion, which was adopted by citizens all over the world. In addition, Rome’s philosophy and literature had a major influence on later Western culture.
In summary, public life in ancient Rome was heavily influenced by politics, religion, economics, culture, and the arts. The citizens of Rome participated in public life by engaging in these activities, and by contributing to the political, economic, and cultural life of the city. Roman culture was influential all over the world, and its legacy still lives on today.
Roman Infrastructure
The Roman Empire was a superpower in its day and its infrastructure was one of its hallmarks. The Romans built extensive and impressive roads, bridges and aqueducts. The roads facilitated trade and communication throughout the Empire, while the bridges and aqueducts provided a reliable supply of fresh water. The aqueducts were particularly impressive and were constructed with great advanced engineering skills.
The Roman cities were also built to impress. The most impressive city was Rome itself, which featured many impressive monuments and buildings, such as the Coliseum and Pantheon. The streets of Rome were also wide and well-paved, making it easier for people to get around the city.
The Roman infrastructure was also important for defense. The city was surrounded by fortified walls, and the roads and bridges were designed to be robust enough to withstand military campaigns. The Romans also developed siege engines to allow them to siege and capture enemy cities.
The Roman infrastructure was an essential part of public life in ancient Rome. It enabled citizens to trade goods, travel quickly and safely, and access fresh water. The impressive monuments and buildings also provided public displays of their wealth and power, which made them a major force in the ancient world.
Roman Law
Law was an important part of public life in Ancient Rome. Roman law was based on the Twelve Tables, which were the first written code of laws in the Western world. These laws regulated many aspects of Roman life, such as property rights, inheritance, marriage, and business. Citizens were expected to obey these laws, and punishments for those who disobeyed could be severe.
The Roman legal system was based on the principle of precedent, meaning that judges were expected to base their decisions on earlier court rulings. This ensured that legal decisions were consistent and that justice was served fairly. Roman lawyers used legal arguments and rhetoric to persuade the court and make their case, and jurors were expected to reach a unanimous decision for or against the defendant.
Roman law was an important part of public life in the city. It ensured that citizens were able to freely engage in business and other activities, knowing that their rights and interests were protected by the law. It also provided citizens with a sense of security and protection, as they knew that they could rely on the justice system if they were ever wronged.
Conclusion
Public life in Ancient Rome was greatly influenced by politics, religion, economics, culture and the arts. Rome was home to many impressive monuments and buildings and had a strong legal system. Its infrastructure enabled citizens to get around the city safely and regularly engage in recreational activities. Religion was also a major part of ancient Roman life, with citizens taking part in public shows of faith. Overall, public life in Ancient Rome was an important part of the city’s history and culture, and its legacy lives on today.