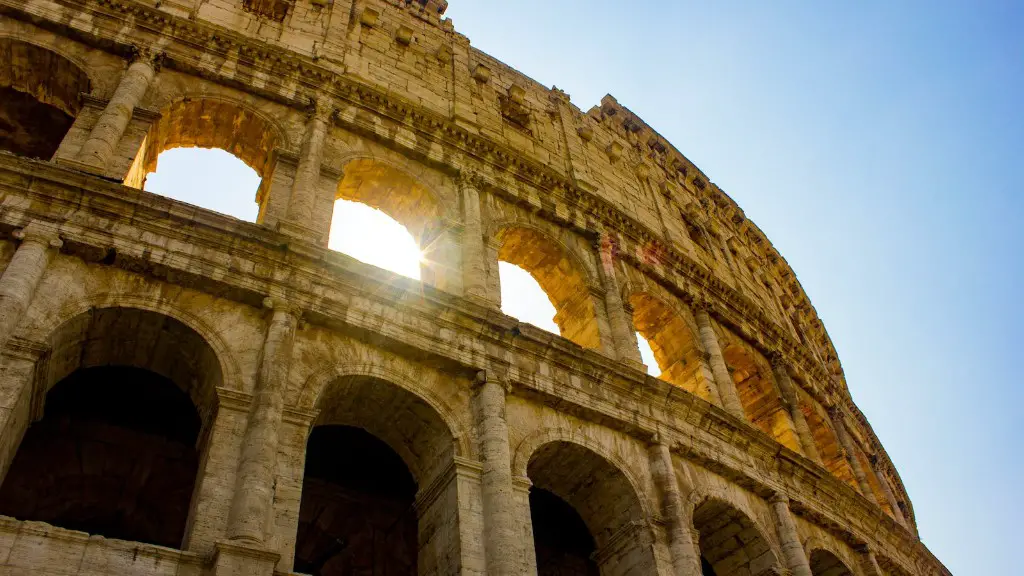
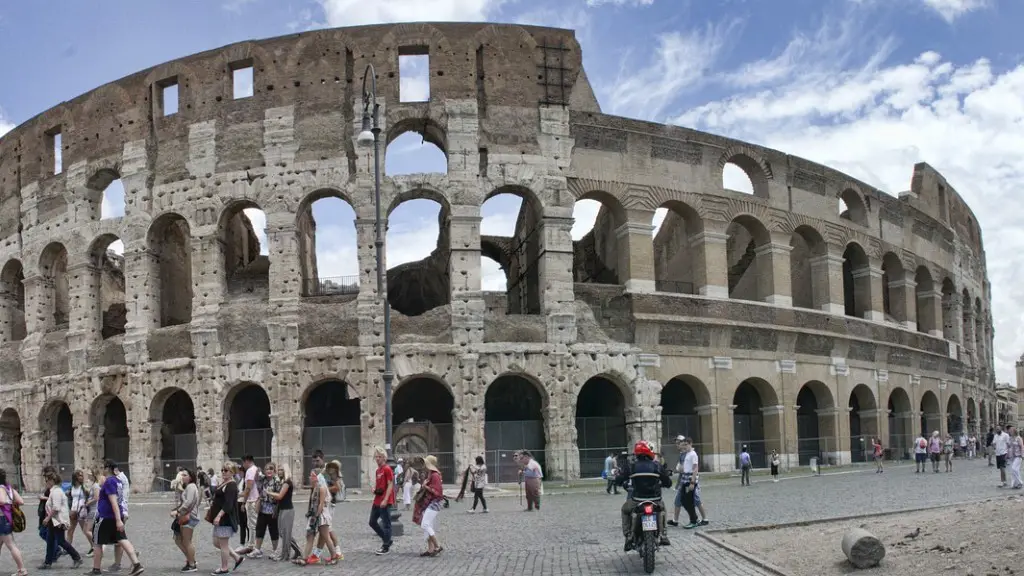
A patrician was a member of the upper class in ancient Rome. The patricians were the wealthier citizens who owned the land. They were the ruling class and held most of the power in the government.
The term “patrician” generally refers to a member of the upper class in ancient Rome. The patricians were originally a group of wealthy landowners who held power in the city. They later expanded to include other members of the oligarchy, such as businessmen and government officials.
What did patrician mean?
The patrician class in early Rome was made up of citizen families who were privileged in comparison to the plebeian class. These families enjoyed special rights and privileges that the plebeians did not, making them a highly sought-after group to be a part of. Over time, however, the distinction between the two classes became lessened and eventually disappeared altogether.
In early Rome, all of the government and religious positions were held by patricians. The patricians made the laws, owned the lands, and were the generals over the army. Plebeians couldn’t hold public office and were not even allowed to marry patricians. This created a lot of tension between the two classes and eventually led to the plebeian revolt in 494 BC.
What is patrician vs plebeian
The patricians and plebeians were the two main social classes in Rome. The patricians were the upper class, while the plebeians were the lower class. The two groups were separated and had different rights and privileges. For example, the patricians could marry anyone they wanted, while the plebeians could only marry someone from their own social class.
Between 616 and 509 BCE, the Etruscans ruled Rome. During this time, Roman society was divided into two classes: patricians and plebeians. Patricians were upper-class citizens who came from a small group of wealthy landowners. The word “patrician” comes from the Latin word pater, which means “father.”
How did Roman patricians make money?
The patricians were the wealthy land-owning noble class in Rome. They often owned slaves who would work their farms for them. The patricians inherited their power and held almost all the important government positions such as the consuls.
The first 100 men appointed as senators by Romulus were referred to as fathers, and their descendants became the patrician class. This fact is also included in an account by Cicero. The appointment of these one hundred men into the Senate gave them a noble status.
Did patricians make laws?
The Roman Republic was established in 509 BC, and with it came a new system of lawmaking. The upper-class patricians were the first to have the right to make laws, but before long the lower-class plebeians were given this right as well. This system of representational lawmaking allowed for a more fair and just society, as all classes of people had a say in the creation of laws.
The head of the household had complete authority over every member of his household. Even when his children became adults, he was still the boss. But, he was also responsible for the actions of any member of his household.
What is an example of patrician
A patrician is a person who comes from a family of high social rank. They are often well-educated and have a sophisticated air about them.
The class structure in ancient Rome was very formal and official. Records of each class were kept, and being wealthy was often not enough to move up through the classes. There were three basic divisions in Roman society: citizens, noncitizens and slaves.
Citizens were those who had full legal and political rights. They could vote, hold office, and own property. Noncitizens were those who did not have full legal and political rights. They could not vote or hold office, but they could own property. Slaves were those who were owned by someone else and had no legal rights.
Was Julius Caesar a patrician?
Caesar was born into a patrician family, the gens Julia, which claimed descent from Julus, son of the legendary Trojan prince Aeneas, supposedly the son of the goddess Venus. Caesar’s family was one of the oldest and most distinguished families in Rome. His father, Gaius Julius Caesar, was a praetor who governed the province of Asia and his mother, Aurelia Cotta, was of noble birth. Julius Caesar himself was born in the annual festival of Lupercalia.
Patricians were a class of elites in ancient Rome. Most of them were wealthy landowners from old families. The class was open to a chosen few who had been deliberately promoted by the emperor. Patricians had a lot of power and privilege. They held high positions in the government and the military, and they owned most of the land. Patricians were also the only people who could become senators.
What did patricians wear
The tunic was a common article of clothing worn by the people of ancient Rome. The patricians, or the upper class, wore white tunics made of wool or linen. The magistrates wore the tunic called augusticlavia, and the senators wore tunics with broad strips called tunica laticlavia. The military people wore shorter tunics. During special occasions, the Romans would cover their tunics with a white woolen coat called a toga.
Plebeians were the working class citizens of Rome who were not members of the patrician or equestrian classes. They were the average citizens who worked hard to support their families and pay their taxes. These working class heroes were an important part of Roman society and contributed greatly to the economy and culture of the city.
Was Julius Caesar a plebeian or patrician?
Caesar’s family background and career were shaped by his membership in the patrician Julii gens. The Julii were one of Rome’s original aristocratic families, which had coalesced in the 4th century BCE with a number of leading plebeian (commoner) families to form the nobility that had been the governing class in Rome since then. Caesar’s career followed the typical path for a young nobleman of his time, beginning with service in the military and the holding of a series of political offices. These experiences prepared him well for the challenges he would face as one of Rome’s most famous and influential leaders.
The Patricians were the ruling men of Rome for as long as anyone could remember. They had to know the laws, fight for Rome, pay taxes, and help rule Rome. They could also be magistrates and take important, powerful jobs.
Final Words
A patrician is a member of the upper echelon of society in ancient Rome. Patricians were typically wealthier than the general population and held more political power.
The term patrician describes a member of the upper class in ancient Rome. The patricians were the original families that settled in Rome, and they held power and influence over the city. The term can also be used to describe someone who is wealthy or elite.