Rome is one of the oldest and most historically significant cities in the world. Situated along the Tiber River in central Italy, Rome was first settled as 300 small villages. Over the centuries, these villages slowly coalesced into a single city, which became the center of the Roman Empire, one of the largest empires in world history. Three features of geography played a significant role in shaping the development of ancient Rome: the Tiber River, the Italian peninsula, and the Mediterranean Sea.
1. Rome is located on the Italian peninsula, which gave the city easy access to the Mediterranean Sea.
2. Rome is situated along the Tiber River, which was a major transportation and trade route in antiquity.
3. The city of Rome is built on seven hills, which provided a strategic advantage in terms of defense and visibility.
What are 3 geographical features of ancient Rome?
Rome was able to grow and ultimately dominate the known world due to several geographic advantages. The mountain ranges of the Alps and the Apennines protected Rome from invasion, while the fertile land and central location made it a hub for trade. The diversity of the population also contributed to Rome’s success.
The Roman Empire was able to expand its military strength due to the fertile soil of the Po and Tiber River Valleys. The diverse selection of crops grown in these valleys allowed the empire to have a food surplus, which was used to feed the population and trade with other societies. The resulting wealth from this trade allowed the empire to further expand its military power.
What are 3 ways that physical geography affected the rise of Roman civilization
The Roman Empire was able to grow and expand due to the fertile soil and mild climate which allowed for surplus olives and grain. This reliable food production allowed for the population to grow, and the trade in olives and olive oil further helped the Roman economy. This shows the importance of having favourable conditions for agriculture in order to maintain a strong and prosperous empire.
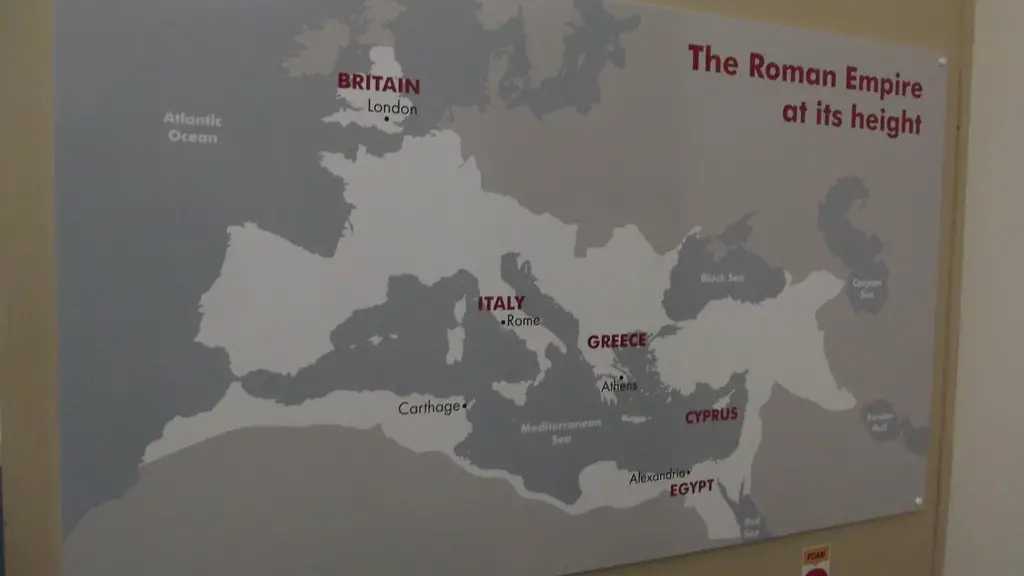
Rome was the dominant power in the Mediterranean region for many centuries. The empire was able to extend its influence far and wide, due to its strategic location and its military might. The boundaries of the empire were largely defined by two great rivers, the Rhine and the Danube to the north, and by the Sahara desert to the south. This allowed Rome to control and influence the trade routes in and out of the Mediterranean, as well as the peoples and cultures in the surrounding areas.
What two geographical features protected Rome?
The Apennines and the Alps served as natural barriers against invaders for the people of Rome. The Apennines stretching from northern to southern Italy and the Alps along the northern border made it difficult for invaders to pass through.
Italy is a country located in southern Europe. It is also a member of the European Union. The country is divided into three parts: Continental Italy, Peninsular Italy, and Insular Italy.
Continental Italy is the largest and most populous part of the country. It is home to the capital city of Rome, as well as other major cities such as Florence and Milan.
Peninsular Italy is a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea. It is home to the cities of Venice and Naples.
Insular Italy is a group of islands that includes the island of Sicily.
How did geography affect where Rome was located?
The Po and Tiber River valleys have rich volcanic soil, making them ideally suited for agriculture. Volcanic ash made the soil near Rome some of the best in all of Europe, which attracted new settlers and caused the Roman population to grow quickly. However, overproduction of grains, olives, and other cash crops led to economic problems.
The mild climate in Rome enabled farmers to grow wheat, grapes, and olives. This abundance of food supported the people and allowed Rome to prosper. While the climate made year-long agriculture possible, Rome also had the advantage to be near water. The Tiber River helped the agricultural system to prosper.
What impact did geography have on the history of Rome quizlet
Rome was founded on the Tiber River, which served as a major thoroughfare between northern and southern Italy. Additionally, Rome’s location across several steep hills made it easier to defend against enemy attacks. These geographical factors helped to contribute to the city’s development and prosperity.
The Roman Republic was a period of political upheaval that was caused by economic stagnation in Rome, slave revolts, and dissension in the military. This led to the fall of the Republic in 133 BC.
What important geographic features does the Roman Empire control?
The legacy of Rome is still very apparent in many aspects of modern life. The legal system, for instance, is based on Roman law, and the Latin language is still used in many academic disciplines. Roman architecture is also still very evident in many modern buildings, especially in cities that were once part of the Roman Empire. Even certain phrases and words that we use in everyday conversation are of Roman origin. So in many ways, the legacy of Rome is still very much alive in the world today.
A functional region is defined as an area surrounding a node or focal point, where a specific social or economic function takes place. Geographers have identified three types of regions: formal, functional, and vernacular. A functional region is also known as a nodal region.
What geographic forms exist in and around Rome
The Seven Hills of Rome east of the river Tiber form the geographical heart of the city. The Aventine Hill is the southernmost of the seven and is most famous for its flowering trees and its gardens. The Caelian Hill is the site of the ancient Roman Forum and the baths of Caracalla. The Capitoline Hill was the political center of the city during the time of the Roman Republic and is now home to Rome’s city hall. The Esquiline Hill is the largest of the seven hills and is home to the Basilica of Santa Maria Maggiore. The Palatine Hill is the center of the seven hills and is the most ancient part of the city, with remnants of the first walls built around Rome. The Quirinal Hill is the site of the official residence of the President of the Italian Republic. The Viminal Hill is the smallest of the seven hills and is home to the Basilica of St. Peter in Chains.
The eight official regions recognized by the Department of Homeland Security are Africa, Asia, Europe, Oceania, the Caribbean, North America, Central America, and South America. These regions are based on the geopolitical divisions of the world map.
Which geographic had the greatest influence on ancient Rome?
Some historians believe that the Roman civilization was even more influential than the Greek civilization. Roman society was based on the concepts of hierarchy and order, while Greek society was based on the concepts of democracy and individualism. The Romans were also able to make improvements to certain borrowed Greek designs and inventions. For example, the Romans invented concrete, which was a stronger and more durable building material than the marble that the Greeks used.
The Roman Empire was founded in 625 BC by Romulus, the legendary founder of Rome. The Period of Kings began with the founding of the Roman Republic in 509 BC and ended with the overthrow of the last Roman king, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, in 508 BC. The Roman Republic was a government founded on the idea of popular sovereignty, in which the Roman people elected their own leaders. The Republic was characterized by a strong central government with a Senate and two consuls, as well as a well-developed system of law and governance. The Republic was also marked by a series of military successes, which expanded the territory of Rome and made it one of the most powerful states in the Mediterranean. The Republic came to an end in 31 BC, when the Roman general Octavian defeated his rivals in the civil war and became the first Roman emperor, Augustus. Augustus and his successors expanded the territory of the empire and ushered in an era of prosperity. The empire reached its greatest extent under the rule of Trajan, who ruled from 98-117 AD. The empire began to decline in the 3rd century AD, due to economic, military, and political problems. The empire was divided into two parts in 395 AD, the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern
Final Words
1. The first feature is the climate. The climate of ancient Rome was perfect for growing crops and for supporting a large population.
2. The second feature is the availability of water. The Roman aqueducts brought water from far away to the city, making it possible for the Roman people to live in an urban environment.
3. The third feature is the location. Rome is located in a very strategic spot, at the crossroads of two major trade routes. This gave the Roman Empire access to a wealth of resources and made it a very powerful force in the ancient world.
The three features of geography that shaped ancient Rome are its location, climate, and resources. Rome’s location allowed it to control trade routes and interact with other cultures. Its climate was mild, which allowed for agriculture. And its resources included fertile land, minerals, and timber. These geographical features helped Rome become one of the most powerful empires in the world.