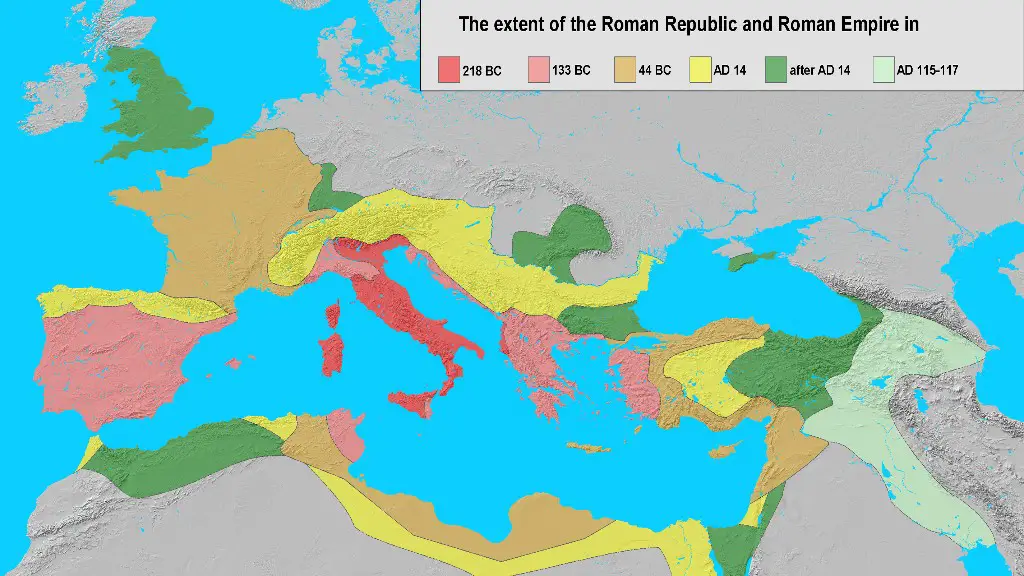
Hydraulic engineering was extremely important to the Romans, as it allowed them to build and maintain a complex system of aqueducts, canals, and reservoirs that supplied water to cities and towns throughout the empire. The Roman Empire was the largest and most complex hydraulic civilization of its time, and its achievement in this area helped to make it one of the most powerful empires in history.
Yes, ancient Rome was a hydraulic civilization. The city of Rome was built on the banks of the River Tiber, and the Roman civilization made full use of the river for transportation, irrigation, and power. The Roman aqueduct system was one of the most impressive feats of engineering of the ancient world, and it allowed the Romans to bring water to their cities from great distances.
Which civilization is known as hydraulic civilization?
Sri Lanka had an efficient hydraulic civilization for a period of thousand years from 200 BC till 1200 AD. Out of its 103 drainage basins, those underneath in the dry zone were successfully irrigated through system of tanks and diversion canals.
Hydraulics in ancient Greece and Rome refer to the use of water to power machines and devices. The term is derived from the Greek word for water, hydro. Ancient Greek and Roman engineers used hydraulics to power a variety of devices, including irrigation systems, canals, and aqueducts.
Irrigation systems in particular made use of the power of water to transport water from one location to another. This was essential for crops and plants, which needed a regular supply of water to grow. Canals and aqueducts were also built using hydraulics, in order to transport water over long distances.
Ancient Greek and Roman engineers were highly skilled in the use of hydraulics. They developed a deep understanding of how water could be used to power devices, and how to design and build systems that made use of this power. This knowledge was passed down through the generations, and hydraulics continue to be used in modern engineering.
What are the 4 hydraulic civilizations
The forced labour for irrigation projects was directed by the bureaucratic network. Among these hydraulic civilizations, Wittfogel listed ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, China, and India and pre-Columbian Mexico and Peru. The primary motive for the development of these civilizations was the need to increase agricultural production in order to support the growing population. In order to achieve this, the rulers of these civilizations resorted to the use of forced labour to construct irrigation systems. This resulted in the development of a class of bureaucrats who were responsible for the management of these irrigation systems. The development of these hydraulic civilizations was therefore largely due to the efforts of these bureaucrats.
Sri Lanka is well known for its hydraulic civilization from the beginning of the 3rd century BC. The hydraulic civilization of Sri Lanka is one of the oldest in the world and dates back to the time of the Mahavamsa. The Mahavamsa is a Buddhist text that is the source of much of our knowledge about the history of Sri Lanka. The hydraulic civilization of Sri Lanka is thought to have begun with the construction of the great tank at Anuradhapura in the 3rd century BC. This tank was built by King Devanampiya Tissa and was one of the largest engineering projects of its time. The hydraulic civilization of Sri Lanka reached its peak in the 1st century BC with the construction of the massive irrigation works of King Dutugemunu. These works included the construction of canals, dams, and reservoirs on a scale that was unprecedented in the ancient world. The hydraulic civilization of Sri Lanka declined in the 2nd century AD with the invasion of the island by the Tamil kingdom of Chola.
Which civilization was the first one to use hydraulic engineering in controlling floods?
The Egyptians were able to use hydraulic technology to plant and irrigate two crops per year, measure the flood, and successfully control flood levels and attempted flood control in the Nile Valley. This was a very impressive feat, and it is one of the reasons why the Egyptians were able to thrive for so many years.
Hydraulic presses are devices that use liquid pressure to generate force. They are often used in industrial settings, such as in the automotive industry, to press and shape metal components. Hydraulic presses work by using a hydraulic cylinder to generate a force that is transferred to the workpiece. The force is generated by the pressure of the fluid in the cylinder, which is typically oil. The oil is pressurized by a pump, and the pressure is released by a valve. The force is then transferred to the workpiece through a piston or a plunger. Hydraulic presses are typically classified by the type of force they generate. The most common type is the hydraulic press, which uses a piston to generate a force that is transferred to the workpiece. Other types of hydraulic presses include the ram press, which uses a ram to generate a force, and the screw press, which uses a screw to generate a force.
Did the Romans use hydraulics?
The Roman civilization was one of the most advanced of its time, and their development of hydraulic systems is a clear indication of that. By using water to power mills, mine for resources, and irrigate crops, the Romans were able to provide for a large population. Furthermore, their use of fire fighting techniques helped to keep their communities safe. Aqueducts were also built in order to bring water to different areas of the Roman Empire. All of these advancements helped to make the Roman Empire one of the most powerful and influential empires of its time.
Joseph Bramah was an English inventor who is best known for his work on the flush toilet and the hydraulic press. He was a highly skilled engineer and is considered one of the fathers of hydraulic engineering. He made many significant contributions to the field of engineering and was awarded the Order of the British Empire in recognition of his work.
What is the origin of hydraulic
Hydraulics is the study of the effects of water in motion. This can include the study of the movement of water in rivers, the ocean, and other bodies of water, as well as the study of how water affects the land. Hydraulics can also involve the study of how water is used in engineering, such as in irrigation, flood control, and dams.
There have been many great civilizations throughout history that have mysteriously disappeared. Some of the most famous are the Mississippians, the Easter Islanders, theKhmer Empire, the Maya, and the Sumerians. Each of these cultures had their own unique customs and way of life.
What caused these civilizations to vanish is still a mystery. Some scientists believe that disease and climate change played a role. Others think that it was due to civil unrest or environmental disasters. Whatever the reason, these cultures are gone, but they have left behind a fascinating legacy.
What are the 5 cradle of civilization?
There are six generally accepted cradles of civilization. They are Mesopotamia, Ancient Egypt, Ancient India, Ancient China, the Caral-Supe civilization of coastal Peru, and the Olmec civilization of Mexico. All of these civilizations have made significant contributions to the world in terms of art, science, technology, and politics.
It is interesting to note that only four ancient civilizations were the basis for continuous cultural development in the same location. These four civilizations were Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus valley, and China. It is fascinating to think about what might have been had the Minoan society on Crete not been destroyed and its cultural traditions and legends not passed into the life of mainland Greece.
Why most of ancient civilizations were considered hydraulic civilizations
Hydraulic civilizations were described as places of agricultural systems that were dependent on the crucial government, directed water systems for irrigation and flood management Wittfogel described Ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, Northern China, India, and pre-Columbian Mexico and Peru as Hydraulic civilizations.
Pascal’s law is the basis for all hydraulic systems. It states that any pressure exerted on an enclosed liquid is transmitted undiminished in all directions. This law is what allows hydraulic systems to function by using a small amount of force to create a large amount of force.
Who proposed the hydraulic origin of the state?
Hydraulic civilizations are those in which water plays an important role in the functioning of the state. Wittfogel argued that many early states were formed as hydraulic civilizations, in which leaders controlled people by controlling the water supply. In these civilizations, irrigation systems were often complex and required centralized management.
Historians have long spoken of the “hydraulic” civilizations — nations and empires with irrigation and intensive water management at their center. These civilizations include Egypt, much of ancient Mesopotamia, the Harappans of South Asia, the Chinese centers of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, and Angkor Wat in southeast Asia.
Irrigation and water management were crucial to the success of these civilizations. Without these technologies, they would not have been able to sustain their large populations and complex societies.
Today, we are facing a new water crisis. With the world’s population projected to reach 9 billion by 2050, and climate change making water availability more unpredictable, we need to find new ways to use and manage water. We can learn from the past and build upon the success of the hydraulic civilizations to create a more sustainable future.
What civilization had running water first
The Minoan civilization of what is now Greece was the first civilization known to use subterranean clay pipes for water supply and sanitation purposes. The Egyptians and the Romans both used water wheels known as ‘norias’ to move water from rivers to raised aqueducts.
The Egyptian civilization stems back to around 3100 BC and is one of the oldest known civilizations. The reason that it developed along the Nile River is largely due to the fact that the river’s annual flooding ensured rich and reliable soil for crops. This allowed for a stable food supply, which was essential for the growth of the civilization. The Nile also served as a means of transportation and communication, which was essential for the development of trade and commerce.
Conclusion
There is some debate over whether ancient Rome can be classified as a hydraulic civilization, but many historians believe that the use of water played a significant role in the development and success of Rome. One of the most impressive feats of Roman engineering is the aqueduct system, which was used to transport water over long distances for public baths, latrines, and fountains. This system was unique at the time and required a high level of technological skill to build and maintain. In addition, the Roman empire was known for its public baths, which were often decorated with mosaics and sculptures. These baths were not only used for hygiene but also for socializing and entertainment. The Romans also made use of water power for mills and other machinery. Overall, it is clear that water played an important role in the everyday life of the Romans and was essential to their wellbeing.
According to the definition of a hydraulic civilization, ancient Rome would not be classified as such. A hydraulic civilization is one that uses water to support a large population, for things such as irrigation, transportation, and domestic uses. Although Rome did have a complex system of aqueducts, this was not enough to make up for the lack of other water infrastructure.