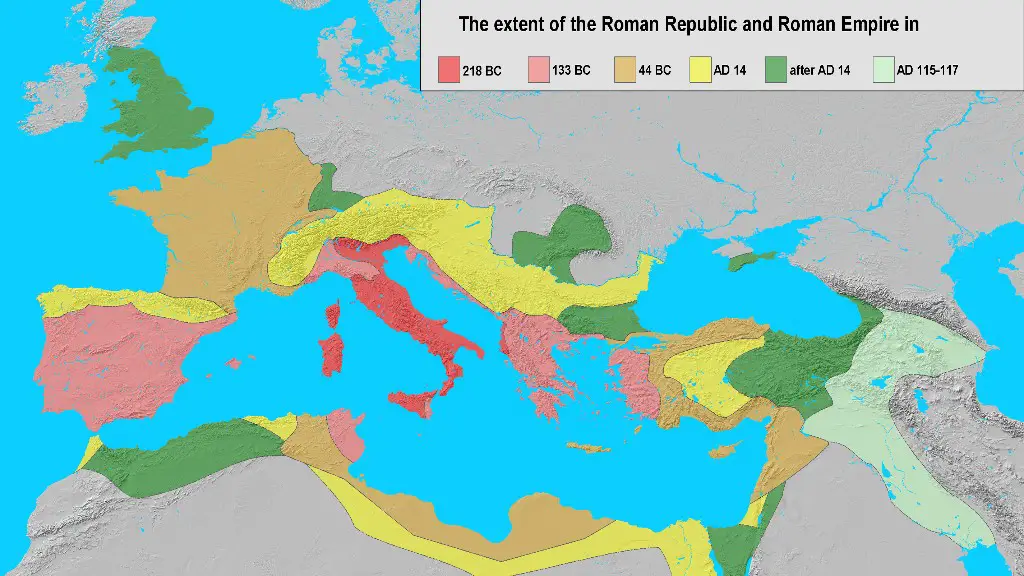
No, ancient Rome and the Roman Empire are not the same thing. Ancient Rome was a period of time in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to become an important center of power in the Mediterranean region. The Roman Empire was a political entity that emerged from ancient Rome and came to dominate the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Asia, and Africa.
No, they are not the same thing. The Roman Empire was the political entity that succeeded Ancient Rome after the latter’s fall.
Is there a difference between ancient Rome and the Roman Empire?
The Roman Republic was a democracy, while the Roman Empire was ruled by a single man. The Roman Republic was also in an almost constant state of war, while the Roman Empire’s first 200 years were relatively peaceful.
Rome was originally a republic, with power resting in the hands of a representative democracy. However, over time, power shifted away from the democracy and towards a centralized imperial authority, with the emperor holding the most power. This transition from republic to empire is one of the most significant events in Roman history.
What is ancient Rome also known as
Rome is one of the oldest cities in the world and has been continuously inhabited for over two thousand years. It is also one of the most influential cities in history, having been the center of the Roman Empire and the home of the Vatican City. Rome is sometimes called the “Eternal City” or the “Capital of the World”.
The Roman Empire was one of the most powerful empires of its time. It was founded by Augustus Caesar in 31BC and ended with the fall of Constantinople in 1453CE. The Roman Empire was known for its military might, its architecture and engineering, and its political and legal system.
Does the Roman Empire still exist?
Although the Roman Empire no longer exists, there are still many modern countries that were once part of it. These include Italy, France, Spain, Portugal, The United Kingdom, Romania, Greece, Egypt, Israel, Syria, Turkey, Lebanon and Tunisia. The capital of the Roman Empire, Rome, still exists today.
In 476 CE, Romulus, the last of the Roman emperors in the west, was overthrown by the Germanic leader Odoacer. This marked the end of the Roman Empire in the west, and the beginning of a new era known as the Early Middle Ages. Odoacer was the first Barbarian to rule in Rome, and his rule ushered in a period of instability and turmoil. The order that the Roman Empire had brought to western Europe for 1000 years was no more.
What was Rome called before empire?
The Roman Republic transitioned to an empire after power shifted away from a representative democracy to a centralized imperial authority. The emperor held the most power in the empire, with the senate and the people having less power than in the Republic.
Augustus (also known as Octavian) was the first emperor of ancient Rome Augustus came to power after the assassination of Julius Caesar in 44 BCE. He was a remarkable leader and managed to transform the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. Under his rule, Rome became a great power and flourished. Augustus was a wise and just ruler, and he is remembered as one of the greatest emperors in history.
What destroyed the Roman Empire
There are many theories about why the Western Roman Empire fell in 476 AD. One of the most popular theories is that the Empire was invaded and overtaken by barbarian tribes.
For centuries, Rome had been losing ground to barbarian groups like the Goths. By the 300s, these groups had advanced beyond Rome’s borders and were making serious inroads into the Empire. In 476, the last Roman emperor was overthrown by a coalition of Goths led by Odoacer.
While there are many factors that contributed to Rome’s decline, the Barbarian invasions were a major factor in the Empire’s ultimate demise.
The Latins were a distinct tribe who migrated to the area during the late Bronze Age. They remained a distinct tribe until around 753 BCE when Rome was founded. Rome started to develop as a city and the Latins remained a distinct group within the city.
What nationality were Romans?
The early Romans were originally a part of the Latin homeland known as Latium. They were Latins themselves and spoke the Latin language. The early Romans were also considered to be Italians by the other Latins.
The people of early Rome were indeed Latins, and they did share an ethnic, linguistic, and cultural identity with the people of other nearby Latin cities. However, there were also some significant differences between the people of Rome and those of other Latin cities. For example, the people of Rome were more militaristic and expansionistic, and they also had a strong sense of Roman identity that was different from the other Latins.
What replaced the Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the continuation of the Roman Empire in its eastern provinces after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 CE. The first truly strong emperor of the Byzantine Empire was Justinian, who ruled from 527 to 565 CE.
Although the evidence suggests that Rome was initially ruled by Etruscan kings, the Romans revolted and established a republic in 509 BC. East of Rome were other tribes speaking languages related to the Romans’ native Latin.
What language did the Romans speak?
During the empire Caesar Latin spread even further and became the dominant language in Western Europe. It remained the dominant language in Europe for centuries, even after the fall of the Roman empire. Latin continued to be spoken by the educated classes in Europe through the Middle Ages and the Renaissance. In the 17th and 18th centuries, Latin began to be replaced by the vernacular languages in many parts of Europe. However, it is still used as the official language of the Vatican City and as a liturgical language by the Catholic Church.
The Byzantine Empire was one of the great empires of the world. It was, however, largely forgotten about by the West until its fall to the Ottoman Turks in 1453. The Empire was a great center of learning and culture, and its influence can still be seen in the Eastern Orthodox Church. The fall of the Byzantine Empire was a tragedy, but it also opened up a new era in world history.
What was the biggest empire in history
The British Empire was one of the largest empires in history and at its peak controlled a territory that covered over 13 million square kilometers. The empire was primarily built through conquest and major territorial expansions during the 18th and 19th centuries. The British Empire began to unravel after World War I and was officially dissolved in the mid-20th century.
Around 10% of Ancient Rome is left today. However, much of it was destroyed over time and what remains is in ruins. The remaining 90% is said to be buried deep inside the earth, around 30 feet below the street level today.
Conclusion
No, they are not the same thing. Ancient Rome was a major political and cultural center in the Mediterranean region during the height of the Roman Republic (c. 509-27 BC), while the Roman Empire was the largest and most powerful political entity in the world during the height of the Roman Empire (c. 27 BC-476 AD).
No, they are not the same thing. The Roman Empire was a political entity that originated after the demise of the Roman Republic. It encompassed a much larger geographical area and last much longer than the Roman Republic.