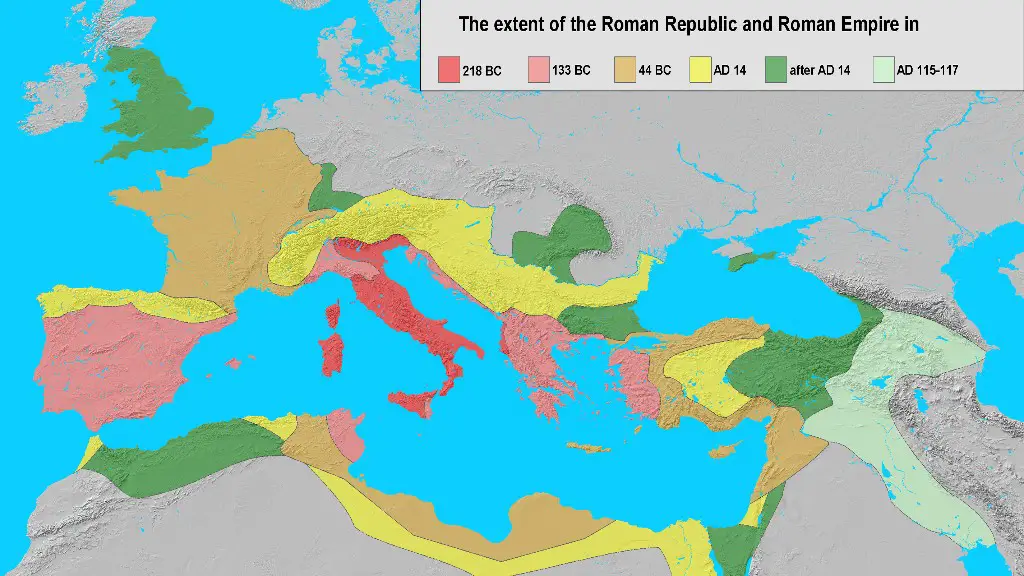
Roads were a vital part of the Roman Empire, allowing for trade, transportation of goods, and movement of troops. The Roman road system was one of the most extensive and advanced of its time. Roman roads were built for durability and efficiency, and continued to be used long after the fall of the Roman Empire.
In ancient Rome, roads were primarily built for the military to facilitate the movement of troops and supplies. The roads were constructed by the army engineers and consisted of a layer of large stones set in the ground and compacted. A second layer of smaller stones was then placed on top and the whole surface was covered with a layer of dirt. This type of construction made the roads very durable and able to withstand heavy traffic.
How did Romans build roads so straight?
The Romans did not have a compass or maps to help them build roads How did they manage it? Surveyors used a tool called a groma This was an instrument that had two pieces of wood nailed together so that they formed a square cross with right-angles in all the corners. The surveyor would sight along one arm of the groma and then walk in a straight line until the other arm was lined up with something else that he wanted to use as a marker. In this way, the surveyor could create a grid of intersecting lines that would help him to map out an area.
The roads that the Roman Empire built were some of the most impressive feats of engineering in the ancient world. These roads were built to last, using a variety of different sized stones that were compacted together to create a strong and stable surface. This allowed them to withstand the heavy traffic of marching soldiers and carts laden with supplies.
Who built the roads in ancient Rome
The Roman military was responsible for building all the roads of the Roman Empire. This was a massive undertaking that required the skills of many specialists. The Roman military employed these specialists to build the roads. This was a very important part of the Roman military’s operations and helped to keep the empire running smoothly.
The Roman roads were built for military purposes and were some of the most advanced engineering feats of their time. The roads were straight, well-built, and able to drain water effectively. They were also built using concrete, which was a new material at the time. The roads allowed the Roman military to move quickly and efficiently across the empire.
Do any Roman roads still exist?
Roman roads were built for military, political, and economic reasons. They were the first long distance roads built in Europe and allowed for a large increase in trade and transportation. Many of these roads are still in use today, though some have been built over by national highway systems. Some of the original Roman roads still have their cobbles, which is a testimony to their durability. These roads are a reminder of the Roman Empire’s engineering prowess and are a significant part of Europe’s cultural heritage.
The Romans were one of the first cultures to develop a sophisticated road infrastructure. They pioneered important aspects of road building, such as tunnel construction, leveling, land excavation and reclamation, and transportation of materials. These techniques have been improved upon over time to build the smooth roads we use today. The Romans were also responsible for developing the first road signs and markings, which have been adopted and adapted by cultures around the world.
How deep were Roman roads?
The next layer was called the statumen, which was a layer of larger stones that were laid on top of the rudus. This layer was packed with mortar to help bind the stones together.
The final layer was called the pavimentum, which was a layer of tightly fitting stone pavers. This layer provided a smooth surface for travel and helped to keep the road from getting too muddy.
Ruts and potholes can be a major problem for modern drivers, but it turns out that the Romans had the same issue! A road discovered in 2015 in Ipplepen, Britain, showed signs of ruts that were caused by horse-drawn carts. This just goes to show that no matter how advanced our technology gets, we still have to deal with the same old problems!
What are 3 facts about Roman roads
Roman roads are an incredible feat of engineering. Not only were they able to be built quickly and safely, but they were able to withstand large amounts of traffic. Merchant used them to transport goods all over the Roman Empire, and soldiers used them to quickly travel large distances. The surface of the roads were cambered so that rain water would run off into the ditches, which helped to keep the roads in good condition.
It seems that the secret to Roman concrete’s strength lies in the way it was mixed. By mixing the calcium carbonate with the pozzolanic material and water at very high temperatures (a process called ‘hot mixing’), the concrete was able to achieve its extraordinary strength.
What materials did Romans use for roads?
Roman roads were built to last and were very effective at doing so. The materials used to build them were extremely strong and the design of the roads was such that they could handle a large amount of traffic without wearing down.
Roman roads were built with several layers, each serving a different purpose. The bottom layer, called the statumen, was made of large stones. This layer helped support the weight of the road and keep the surface level. The next layer, called the rudus, was made of gravel mixed with concrete. This layer provided a smooth surface for travelers. The top layer, called the nucleus, was made of sand and smaller gravel mixed with concrete. This layer gave the road a smooth, finished surface.
Why don t we use Roman concrete today
Ancient Rome was known for its impressive architecture and engineering, many of which were made possible by the use of concrete. This material was developed using a Roman recipe that included seawater, which helped to give it extra strength. However, modern cement is not made using this method and as a result, it does not have the same compressive strength as its ancient counterpart. This means that it would not be able to withstand the same amount of stress and wear and tear.
The durability of Roman concrete has long been a mystery to historians and scientists. In particular, they are baffled by the concrete that was used to construct ancient harbors. Even after two thousand or more years of being pummeled by saltwater, the harbors are largely intact.
What is the secret to Roman construction?
The study found that Romans actually relied on a process called “hot mixing” to whip up their hyper durable concrete. The benefits of hot mixing are twofold, according to MIT professor of civil and environmental engineering Admir Masic. Hot mixing allows for a more homogeneous mixture, which leads to a stronger and more durable concrete. It also allows the concrete to set more quickly, so that it can be used sooner.
What the Romans did was amazing for their time, but modern engineering has improved on their design in many ways. We now have materials and construction techniques that allow us to build roads that are much stronger and longer lasting, while carrying far more traffic than the Romans could have ever imagined.
How did the Romans transport water uphill
Aqueducts were an amazing feat of engineering for the time period. They were able to transport fresh water to highly populated areas. This was a great boon to the people living in those areas.
While it’s true that the Pompeii and the UK’s Devon wheel ruts are similar, it’s also important to remember that these two cultures existed in different time periods. The Pompeii repairs suggest that road maintenance was a regular occurrence in that culture, while the lack of repairs in the Devon wheel ruts points to a culture that didn’t prioritize road maintenance to the same degree.
Final Words
The ancient Romans built roads by first surveying the land to find the most efficient route. They then cleared the land of any obstacles and prepared the ground for construction. Next, they built a foundation of large stones, which was covered with smaller stones and gravel. Finally, they smoothed the surface and added drainage to prevent flooding.
The roads in ancient Rome were made by a labor force of soldiers and slaves. The roads were built for the purpose of transportation and trade. The roads were made of stone, dirt, and gravel.