The Roman Republic existed from 509 BC to 27 BC. The Republic was founded after the Roman Kingdom was overthrown by the Roman people. The Republic lasted until it was replaced by the Roman Empire.
Ancient Rome was a republic from 509 BC to 27 BC.
How long was Rome a republic before it became an empire?
The Roman Republic was founded in 509 BC, and lasted for over 450 years. It was eventually replaced by the Roman Empire in the wake of Julius Caesar’s rise and fall in the first century BC. Augustus, the first emperor of Rome, ushered in a golden age of peace and prosperity. However, the Roman Empire ultimately declined and fell by the fifth century AD.
The end of the Republic was marked by the final defeat of Mark Antony alongside his ally and lover Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the Senate’s grant of extraordinary powers to Octavian as Augustus in 27 BC. Augustus was the first Roman emperor, and his rule marked the end of the Republic.
Why did Rome switch from a republic to an empire
There were a number of factors that led to the decline of the Roman Republic. One was the increasing gap between the rich and the poor. The rich were getting richer and the poor were getting poorer, and this led to a lot of social unrest. Another factor was the rise of powerful military leaders. These leaders began to challenge the authority of the Roman Senate, and this led to a series of civil wars. In the end, the Roman Republic was transformed into an empire.
The Roman Republic lasted for over 1000 years. It began in 753 BCE, and much like other civilizations started as a small town and grew into larger cities. Early Rome was ruled by kings that ruled for life. Eventually Romans overthrew the monarchy and created the Roman Republic in 509 BCE.
Why did Rome stop being a republic?
The fall of Rome can be attributed to a number of factors, including economic problems, government corruption, crime, and the rise of Julius Caesar as emperor. Rome’s continued expansion resulted in a need for more money and revenue, which led to increased taxes and government debt. Government corruption was also a major problem, with officials often pocketing public funds for personal gain. This led to a loss of faith in the government, which contributed to the decline of the Republic. Additionally, crime was rampant, with private armies often terrorizing citizens. The rise of Julius Caesar as emperor was also a factor, as his rule led to a decline in the power of the Senate and the rise of autocracy.
The most straightforward theory for Western Rome’s collapse pins the fall on a string of military losses sustained against outside forces. Rome had tangled with Germanic tribes for centuries, but by the 300s “barbarian” groups like the Goths had encroached beyond the Empire’s borders. The Roman Empire was not built to withstand such attacks, and over time, the toll of these defeats proved too much for the Empire to bear.
Who destroyed the Roman Republic?
Augustus Caesar is considered one of the most important figures in Roman history. He played a critical role in the transition from the Roman Republic to the Roman Empire. Augustus was the first Roman Emperor and helped to stability to Rome after a period of political turmoil. He also reformed the Roman government and strengthened the economy. Augustus was a great military leader and expanded the Roman Empire significantly.
Rome was a Goldilocks city, not too democratic, not too monarchical, with a well-ordered military system and a religion in which the right people were firmly in control. That sort of analysis appeals more to modern political science with its interest in institutions.
Rome was successful because it had the right mix of democracy and monarchy, and because its religious and military institutions were well-ordered. This analysis is appealing to modern political scientists because it emphasizes the importance of institutions.
Who ruled over Rome before the republic
Before the Roman Republic was formed, Rome was ruled by kings. Roman history tells of seven kings starting with Romulus in 753 BC. Each king was elected by the people for life. The king was very powerful and acted as the leader of both the government and the Roman religion.
Augustus was the founder of the Roman Empire and the first emperor of Rome. He was born Gaius Octavius Thurinus on September 23, 63 BCE, in Rome. His father, Gaius Octavius, was a senator and his mother, Atia, was the niece of Julius Caesar. Augustus was educated in Latin and Greek and was a skilled poet and orator.
In 44 BCE, Julius Caesar was assassinated and Civil War broke out. Augustus sided with Caesar’s friend, Marcus Antonius (Mark Antony), in the war against Julius Caesar’s nephew, Octavian. Antonius and Octavian were the two most powerful men in Rome. In 31 BCE, the two men’s armies met at the Battle of Actium and Octavian emerged victorious. Antonius and Cleopatra, Queen of Egypt, committed suicide and Octavian became the sole ruler of Rome.
Octavian was renamed Augustus by the Roman Senate in 27 BCE and he ruled Rome as an autocrat. Augustus reformed the Roman government and the military, and initiated many public works projects. He also expanded the Empire, annexing Egypt and parts of present-day Spain, France, and Croatia. Augustus was a skilled politician and
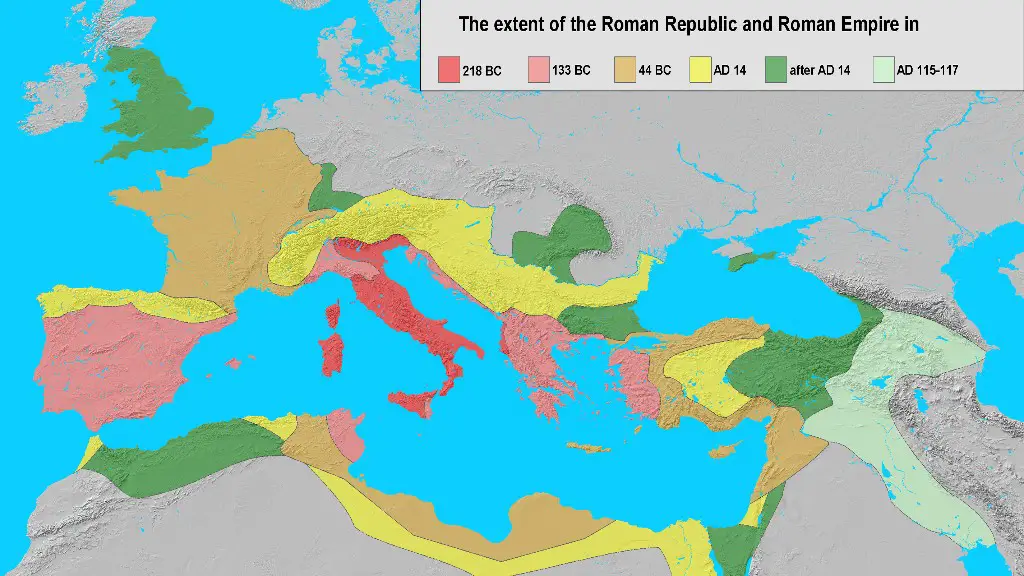
Was the Roman Empire bigger than the Roman Republic?
The Roman Empire was one of the most powerful empires in history. It ruled over a large area of the world for centuries. During its time, Rome was the biggest and most powerful city in the world. The empire was a major cultural force in the world and had a big impact on the development of Western civilization.
The Roman Republic officially came to an end in 27 BCE when Octavian was made the princeps, or the “first citizen”. This title was originally intended to make it appear as though Octavian had limited power, but in reality he had become the autocratic ruler of Rome and the first emperor of the Roman Empire. This marks the end of the Roman Republic and the beginning of the Roman Empire.
What is the longest empire in history
Empire is a coffee table book about the largest empires in human history. It is divided into two parts. The first part looks at ancient empires and the second part looks at modern empires. The book argues that although there have been many great empires in history, the largest and most enduring empire is Japan.
Japan has existed as an empire for over 2600 years if we count legendary emperors, and still 1743 years and counting if we start from the first historical emperor. The book explains how Japan has been able to maintain its empire for so long, despite challenges from both internal and external forces.
Empire is an interesting and informative book that will appeal to anyone with an interest in history or in the study of empires.
It is incredible to think that only around 10% of Ancient Rome still exists today. The vast majority of it has been destroyed over time, and what remains is mostly in ruins. The remaining 90% is said to be buried deep underground, around 30 feet below the street level of today. It is amazing to think about all the history and culture that has been lost over time, but it is also fascinating to imagine what might still be waiting to be discovered.
How long did the Roman Empire last before it split?
The Roman Empire is one of the oldest empires in history. It can be divided into three distinct periods: The Period of Kings (625-510 BC), Republican Rome (510-31 BC), and Imperial Rome (31 BC – AD 476). Each period has its own unique history and there are many famous historical figures associated with each period.
The Roman Republic was in trouble. It had three major problems. First, the Republic needed money to run. Second, there was a lot of graft and corruption among elected officials. Finally, crime was running wild throughout Rome.
Who was the last king of Rome
Lucius Tarquinius Superbus was the last king of Rome. He was a controversial figure, and some scholars believe he was a historical figure. He was known for his tyrannical rule and for his many wars. He was eventually overthrown by the Roman people and exiled from Rome.
The Roman Republic and the Roman Empire were two very different societies. The Roman Republic was a democratic society, while the Roman Empire was run by only one man. The Roman Republic was also in an almost constant state of war, while the Roman Empire’s first 200 years were relatively peaceful.
Conclusion
Ancient Rome was a republic for 482 years.
Ancient Rome was a republic for over 500 years. During that time, it was one of the most powerful empires in the world. The Republic fell when Julius Caesar was assassinated and Civil War broke out.