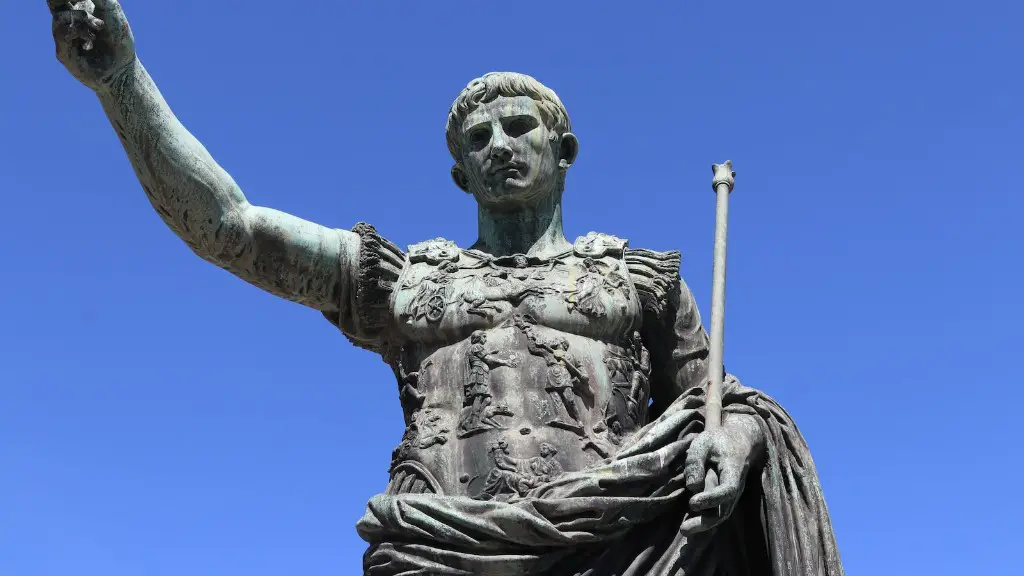
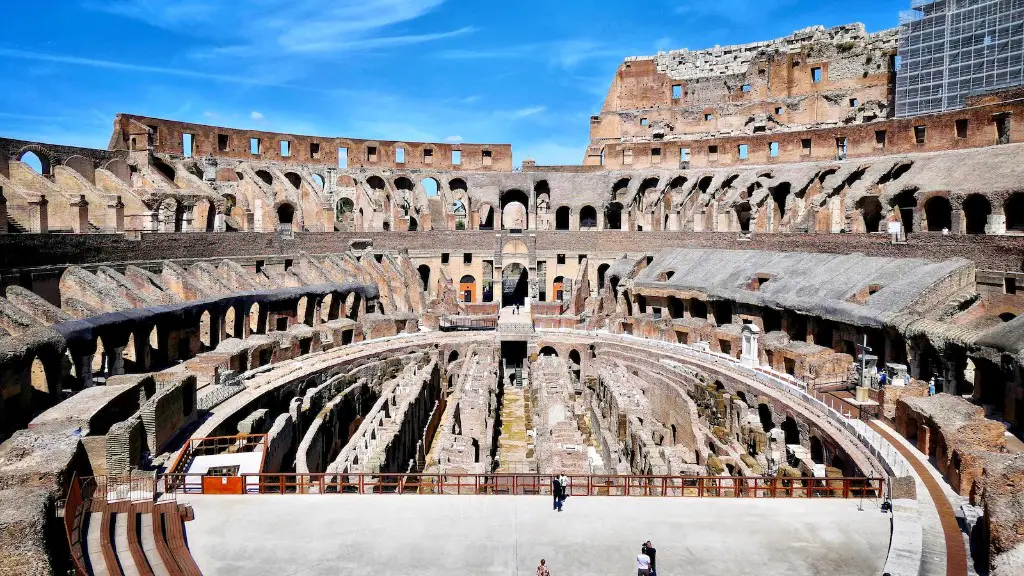
Ancient Rome was one of the most powerful empires in the world for centuries. While the Roman Republic was founded on principles of fairness and equality, the empire that followed was often brutal and dictatorial. Many of Rome’s great leaders, such as Julius Caesar and Augustus, were military dictators. Rome’s emperors often persecuted minorities, such as Christians, and used their power to enrich themselves and their cronies. In spite of all this, Ancient Rome was a remarkable civilization that made lasting contributions to art, literature, law, and architecture.
Although Rome was considered a fair society, there were still many inequalities within its citizens. The poor were often treated unfairly and were not given the same opportunities as the rich. There were also slaves who were treated unfairly and had no rights.
Was there equality in ancient Rome?
Women in ancient Rome were not seen as equals to men before the law. They received only a basic education, if any at all, and were subject to the authority of a man. Traditionally, this was their father before marriage.
The Roman Empire was one of the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of the world’s population at the time. It covered around 5 million square kilometres (19 million square miles) at its height in AD 117. The Roman Empire was a major political and cultural force in the Western and Eastern worlds for centuries.
Was everyone in Rome treated equally
The patricians were a small group of wealthy landowners who had most of the power in Rome. They made the laws and controlled the government. The next largest group was the plebeians. The plebeians were the common people of Rome. They did not have much power, but they could vote and serve in the army. The largest group was slaves. Slaves were people who had been captured in war or sold into slavery by their families. They had no rights and were owned by the patricians.
The rampant bribery and corruption led the commoners to distrust the Senate. Many people were brought back as slaves from Rome’s conquests, which created an influx of cheap labor and hurt the lower classes. This disrupted the agricultural system and caused many problems for the people.
How many genders did the Romans have?
The Romans had a binary sense of gender: there were men and women, and anyone who feel in between those categories was likely to be killed as a child if they displayed signs of both sexes. This was likely due to the fact that the Romans saw gender as a strict dichotomy, and anyone who did not fit perfectly into one category or the other was seen as a threat to their worldview. As a result, children who displayed any signs of both genders were usually killed at birth or shortly thereafter.
The Roman Republic was a complex government that was neither a monarchy nor a direct democracy. It had democratic features, but was essentially a society dominated by a select group of wealthy aristocrats. This class of elites held most of the power in the government and society, and used it to maintain their own position and interests.
What percent of ancient Rome was poor?
The elite class in ancient Sparta was very small, consisting of only a few wealthy individuals. This tiny group made up just 06% of the Spartan population. The society also had an army that made up 04% of the population. The majority of the Spartan populace was made up of the poor masses, who made up an overwhelming 99% of the population.
One of the most significant contributions of Rome to Western Civilization was the establishment of legal culture. Roman law was largely public, and jurists created formalities such as legal language and procedure that would come to define European law for centuries. This helped to create a more ordered and just society, and the lasting legacy of Rome’s legal culture is still evident in the modern world.
Were Romans barbaric or civilized
The above-listed amenities were some of the many things that the ancient Romans were known for. They were a highly advanced and civilized people who had a great impact on the world that we know today.
The code of ideal behavior for Roman women was based on the concept of the matrona, or respectable married woman. This ideal was codified in both written and unwritten laws and social norms, and it prescribed that a woman’s primary responsibilities were to her husband, her family, and her home. Women who defied this stereotype, by for example working outside the home or engaging in public life, often found themselves cast out from society.
How did Romans justify slavery?
The Romans did not think slavery was a bad thing and so they did not see any reason to justify it. Slavery was the consequence of a culture being conquered and people were regarded as captured valuables just like anything else.
Slave under Roman law had no personal rights and were more like property of their masters. They could be bought, sold, and mistreated at will. They were unable to own property, enter into a contract, or legally marry. While this may seem harsh, slaves did have some protections under Roman law. For example, masters were not allowed to kill their slaves without just cause and if a slave was hurt by a free person, the slave’s owner could file a claim against the offender.
What ruined the Roman Empire
The most straightforward theory for Western Rome’s collapse pins the fall on a string of military losses sustained against outside forces. Rome had tangled with Germanic tribes for centuries, but by the 300s “barbarian” groups like the Goths had encroached beyond the Empire’s borders. In 378, the Roman army suffered a crushing defeat at the Battle of Adrianople against the Goths, a victory that signaled the beginning of the end of the Roman Empire.
There were many factors that led to the fall of the Roman Empire. They include economic crises, barbarian attacks, farming issues from exhausted soil due to over-cultivation, inequality between the rich and the poor, detachment of local elites from public life, and economic recession as a result of overreliance on slave labor.
Was Rome destroyed in a day?
The Roman Empire was one of the largest and most powerful empires in history. It stretched across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East, and was home to some of the most technologically advanced and culturally wealthy societies in the world. However, beginning in the 3rd century AD, the empire began to disintegrate, and by 476 AD, it had fallen completely.
There is no single event or individual that can be blamed for the fall of Rome. Instead, it was a gradual process that happened over hundreds of years. There were many contributing factors, including economic problems, political unrest, barbarian invasions, and a decline in moral values.
Although the Roman Empire ultimately fell, its legacy has endure. The Roman system of government, law, and architecture has shaped the Western world in many ways and is still evident in modern times.
The age of consent for marriage was 12 for girls and 14 for boys in Roman times. Most women married in their late teens to early twenties. However, noble women married younger than those of the lower classes. An aristocratic girl was expected to be a virgin until her first marriage.
How common was homosexuality in Roman times
In the Roman Empire, it was considered normal and acceptable for freeborn men to be interested in both male and female partners. This was due to the fact that Roman society was quite tolerant of different sexual orientations. In fact, many Roman men even had same-sex relationships with partners of the appropriate social status.
In ancient times, girls were considered marriageable at the age of twelve. This meant that they were considered adults and could be married off to someone. Today, the legal age for marriage varies from country to country, but is usually around eighteen for women. This is likely because girls were not seen as capable of handling the responsibilities of marriage and family life until they were a bit older.
Final Words
There is no definitive answer to this question; it is a matter of interpretation. Some historians believe that ancient Rome was a fair society, while others contend that it was not. What is certain is that Rome was a complex and stratified society, with a large number of social classes and a great deal of social inequality.
The jury is still out on how fair ancient Rome was. Some historians believe that the ruler at the time, Julius Caesar, was a fair and just ruler. Others believe that he was a tyrant who didn’t care about the people. We may never know for sure.