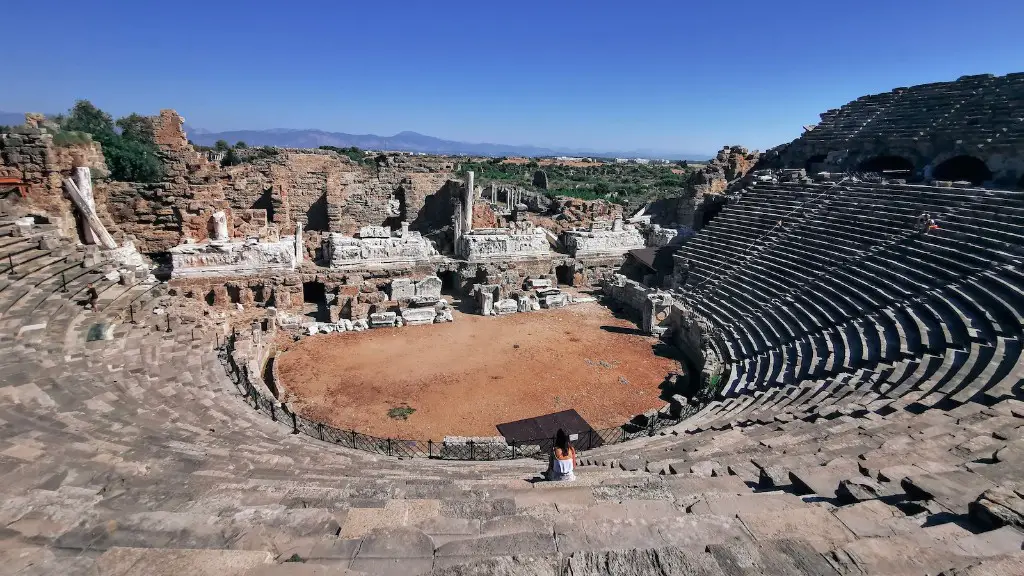
Between the classical period until the empire there was a decline in cultural and literary production in Rome. This was not a total decline however, historians have noted three specific areas in which there was significant decline: (1) in the quality of Latin literature, (2) in the amount of originality in architectural design, and (3) in the painting of portraits and wall-paintings. What was happening during this time to cause this decline?
Ancient Rome was founded in 753 BCE by the brothers Romulus and Remus. It grew through conquest, first of the Italic peoples by the Romans, then of the Mediterranean peoples by the Roman Empire. With the expansion of the empire, Roman culture and society spread throughout the Mediterranean basin and Europe.
What helped ancient Rome grow?
The Po and Tiber River Valleys have a long history of agriculture. The soil is very fertile and has allowed for a diverse range of crops to be grown. This has resulted in a food surplus for the Roman Empire, which has used this to its advantage. The surplus has allowed the empire to trade with other societies and to expand its military strength.
The Roman Republic was a time of great peace and prosperity. However, over time, tensions began to build up within the government. These tensions eventually led to civil wars between different factions, which ultimately led to the transformation of the republic into an empire. While the Roman Republic was a great time in history, it is clear that its internal tensions ultimately led to its downfall.
How did Rome get so advanced
The Romans were able to achieve high levels of technology due to their borrowing of technologies from the Greeks, Etruscans, Celts, and others. With limited sources of power, the Romans were still able to build impressive structures, some of which have survived to this day. This is a testament to the Roman engineering and construction skills.
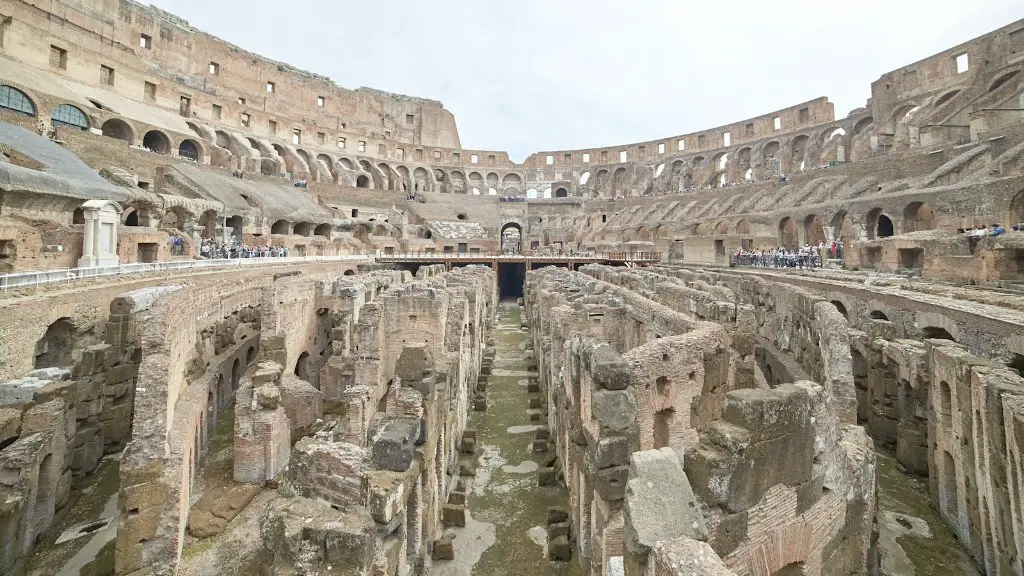
The Roman Empire was one of the largest empires in history. It was founded when Augustus Caesar proclaimed himself the first emperor of Rome in 31BC and came to an end with the fall of Constantinople in 1453CE. An empire is a political system in which a group of people are ruled by a single individual, an emperor or empress. The Roman Empire was known for its military might, engineering achievements, and architecture, as well as for its government, law, and literature.
How did Rome first expand?
The Roman Republic’s first significant expansion came in 396 BC, when it defeated and captured the Etruscan city of Veii. This was a major turning point in Roman history, as the Republic began to assert its power in the region. The capture of Veii also signaled Rome’s emergence as a major player in the politics of the Mediterranean.
The Roman Empire developed because of the ineffective dictatorship of Caesar, his assassination, the civil war that followed, and the rise to power of Octavian. After defeating Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (Pompey the Great), Julius Caesar declared himself dictator of Rome. He ruled as dictator for a short time before being assassinated in 44 BCE. This led to a civil war between Caesar’s supporters and his enemies. Octavian, Caesar’s nephew, eventually emerged victorious and became the first Roman Emperor.
What caused the Roman Empire to rise and fall?
The most straightforward theory for Western Rome’s collapse blames a string of military losses on outside forces. Rome had tangled with Germanic tribes for centuries, but by the 300s “barbarian” groups like the Goths had encroached beyond the Empire’s borders. In 410, the Visigoths sacked Rome, and three years later the Vandals sacked the city of Carthage. The Empire was also beset by economic problems and overreliance on slaves.
The Roman Empire was one of the most powerful empires in history. A combination of law and engineering, military force, and social legislation allowed the empire to maintain its power for centuries. Exceptional leaders also contributed to the success of the empire.
What were the 3 biggest events in Roman history
Ancient Rome was one of the most powerful empires of its time. Major events in its history include the sack of Rome by the Visigoths in 410 AD, the end of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD, and the fall of the Byzantine Empire to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD.
1) Rome was founded in 735 BC. However, there is a belief that it was founded in 753 BC by Romulus.
2) In Rome, cats are free to roam around.
3) The Roman’s eyes were bigger than their stomach. This is because the Roman empire was very large and they wanted to conquer more land.
4) Men could only wear togas. This was a traditional clothing worn by men in Rome.
5) Women wore stola’s. This was a traditional clothing worn by women in Rome.
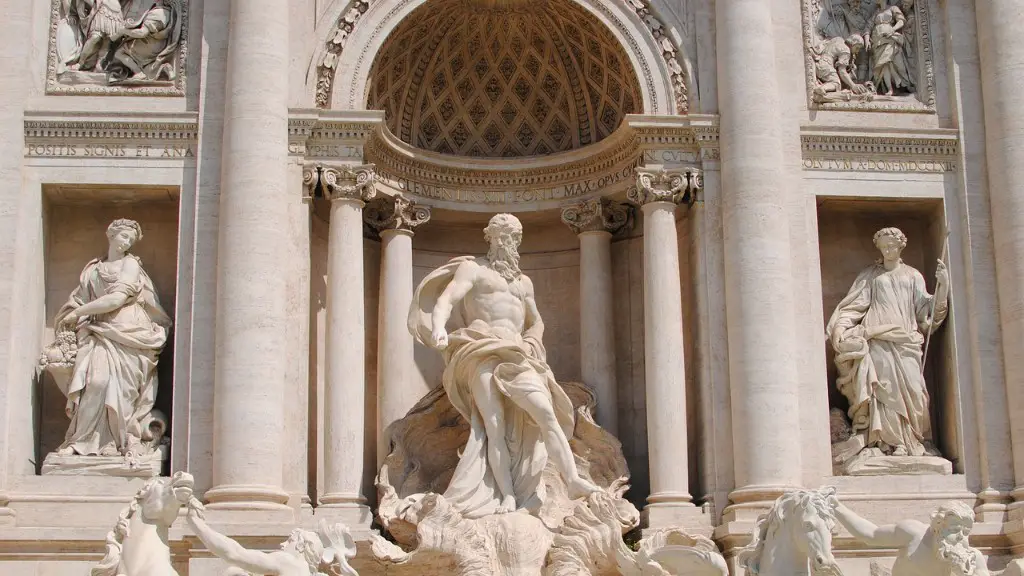
6) The coins in the Trevi Fountain are there for good luck.
7) Roman breathalyzer was invented in Rome. This was used to test whether a person was drunk or not.
8) Colosseum casualties were usually animals or slaves.
How did the Roman Republic rise?
The event that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic was the overthrow of the Etruscan conquerors in 509 BCE. The Etruscans, who were centered north of Rome, had ruled over the Romans for hundreds of years. When the Romans overthrew their Etruscan conquerors, they established a republic, a government in which citizens elected representatives to rule on their behalf. This system of government would go on to be extremely influential, shaping the governments of many countries that came after.
The Persian Empire was one of the largest empires in history. The empire was founded by Cyrus the Great and expandeved to include parts of Central Asia and Egypt. The Han Dynasty was another large empire in history. The Umayyad Caliphate was even larger, stretching from Spain to India. The Mongol Empire was the largest empire in history, covering much of Asia and Eastern Europe. The Ottoman Empire was also quite large, controlling much of the Middle East and North Africa. The Spanish Empire was large as well, controlling much of South America. The Russian Empire was also large, covering much of Europe and Asia. Finally, the British Empire was the largest empire ever, controlling huge swathes of territory around the world.
Why did Rome fail
The Roman army was one of the most powerful military forces in the world for centuries. However, by the 400s AD, the army was becoming overstretched and needed more soldiers than they had. Without adequate protection or money to supply it, the city of Rome finally fell to Germanic Tribes in 476 AD. This was a huge blow to the Roman Empire and led to its decline.
One of the many factors that contributed to the fall of the Roman Empire was the rise of a new religion, Christianity. The Christian religion, which was monotheistic, ran counter to the traditional Roman religion, which was polytheistic (many gods). This religious division would have led to social unrest, and would have been one of the many factors that contributed to the decline of the Roman Empire.
How long was Rome a superpower?
The Roman Empire was an incredibly influential and powerful civilisation that lasted for more than 1000 years. They were known for their grandiose architecture, their advanced engineering and their vast army. The Roman Empire was a major force in the world for centuries, and their legacy is still evident in many aspects of modern life.
Longevity has increased steadily through history and is expected to continue doing so. Life expectancy at birth was a brief 25 years during the Roman Empire, it reached 33 years by the Middle Ages and raised up to 55 years in the early 1900s. However, currently, the global average life expectancy is 72 years. The main contributing factors to this increase are better nutrition, sanitation, and medical care. Additionally, as our understanding of the human body and diseases continue to improve, life expectancy will likely continue to increase.
What ended the Romans
The West was severely shaken in 410 when the city of Rome was sacked by the Visigoths. This event led to the fall of Rome in 476 when the German chieftain Odoacer deposed the last Roman emperor of the West, Romulus Augustus. The sack of Rome was a turning point in history and had a profound impact on the West.
There’s no doubt that the Roman Empire was one of the most influential empires in history. Here are 13 things that the Romans did for us that we still use or benefit from today:
1. Fast food – It might seem a modern marvel, but the Romans were the first to introduce street stalls and ‘food on the move’ as we might think of it today.
2. Advertising and trademarks – The Romans were also responsible for creating both advertising and trademarks as we know them.
3. Plumbing and sanitation – The Romans are credited with developing the first comprehensive system of plumbing and sanitation.
4. Towns – The Roman town model is still evident in many modern towns and cities.
5. Architecture – Roman architecture is some of the most iconic and recognizable in the world.
6. Roads – The Roman road network was the most extensive and sophisticated of its time.
7. Our calendar – The Roman calendar formed the basis of the modern calendar that we use today.
8. The Latin language – Latin was the language of the Roman Empire and has had a lasting legacy.
9. The concept of rights – The Romans were the first to codify the concept of individual rights.
Final Words
The Roman Republic was founded in 509 BC by Romulus and Remus, two of the sons of Mars, the god of war. The twins were raised by a she-wolf until they were grown. Romulus killed Remus and is said to have then founded Rome. The Roman Republic grew by conquest. The Roman army was very strong and conquered many lands. The Roman Republic became an empire under the rule of Augustus Caesar in 27 BC. Augustus was the first emperor of Rome.
The ancient Rome grew by expanding its territory through conquest, by forming alliances and treaties with other city-states, and by establishing colonies. The Rome also became prosperous through trade and commerce. All of these factors made ancient Rome one of the most powerful empires in the world.