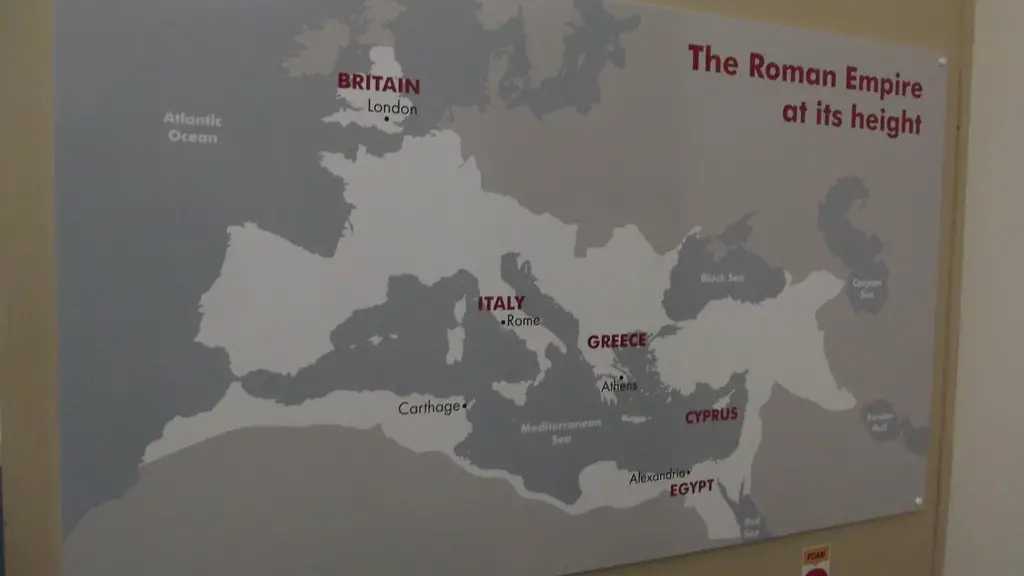
The Roman Republic was, arguably, one of the most powerful empires in the ancient world. At its peak, the empire controlled extensive territory spanning from Northern Europe to North Africa and from the Atlantic Ocean to the Euphrates River. Trade played a major role in the Republic’s prosperity, with Rome exporting a variety of goods throughout its vast territories and, in turn, importing goods from other regions. In order to facilitate trade, the ancient Romans developed an extensive network of roads and waterways.
The ancient Romans traveled for trading by using a network of roads and waterways.
How did the Romans travel to trade?
The Romans used their network of roads and waterways to transport goods from one country to another. The Romans traded with Britain for silver, which they used to make jewellery and coins, and wool, which they used to make clothes.
Ancient Rome’s main trading partners were Spain, France, the Middle East, and North Africa. Since farming was a large part of the Roman economy, many of the exports were food or products made from crops. Grapes, oil, and grain were a few of the major exports.
What mode of transportation would most Roman traders use
A chariot is a two-wheeled cart pulled by horses. You would ride in these standing up. This was the most common and preferred form of transportation because of how quickly chariots could travel.
At its height during the 100s ce, the Roman Empire ruled all the lands that ringed the Mediterranean Sea. The expansion of the empire had given the Romans control of trade routes as well as territory. Traders traveling by land and sea connected people and goods throughout the empire. This made the Roman Empire one of the most prosperous empires of its time.
What are some facts about Roman trade?
There were many important trade items during this time period, which included metals and olive oil from Spain and Africa, grain from Egypt, Africa and the Crimea, spices and silks from the east and wine from France and Italy. These items were carried in large jug-like red clay amphoras on square-sailed merchant ships.
Whilst the Romans are celebrated for their roads, it was actually much cheaper to transport goods by sea rather than by river or land. The cost ratio was approximately 1:5:28, meaning that it was five times cheaper to transport goods by sea than by river, and 28 times cheaper than by land. This was due to a lack of land transport innovation, meaning that goods were transported across the Roman world but there were limitations caused by a lack of land transport innovation.
How did the Romans transport and communicate across the empire?
The Roman courier service was an essential part of the empire’s communication and transportation infrastructure. Couriers would transport messages, officials, and tax revenues from one province to another, ensuring that the empire’s vast territory could be effectively governed. The courier service was highly efficient and reliable, making it an invaluable tool for the Roman Empire.
The Silk and Spice Routes were the main arteries of contact between the various ancient empires of the Old World. These routes allowed for the transport of goods over vast distances, either by pack animals or by seagoing ships. The goods transported along these routes were often luxury items, such as silk and spices, which were highly prized by the empires of the Old World.
What are the two types of transportation they used during the ancient trade Why
Transportation has come a long way since ancient times. People used to craft simple boats out of logs and walk or ride animals to get around. Later, they invented wheeled vehicles to make traveling easier and faster. Nowadays, there are all sorts of transportation options available, from cars and buses to trains and planes. Waterways and roads have also been improved and expanded to accommodate the increasing needs of modern society.
Roman roads were one of the major tools of the Roman Empire. They facilitated trade and travel and served Rome’s successor states just as they had served Roman legions and couriers centuries before. Even as late as the Renaissance, roads that were 1,000 years old were still in use.
Did the Romans have transport?
There are many ways that the Ancient Romans traveled, including by carriage, chariot, walking, riding horses, and riding on a litter. Each method of transportation had its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best method for each individual traveler depended on many factors, including the distance to be traveled, the time available, and the traveler’s budget.
The importation of goods was a major part of the Roman economy, and importers were among the wealthiest citizens of the empire. The Roman coinage system was one of the most developed in the ancient world, and it was used extensively in trade.
What was Roman transport based on
Roman transport in this era was very efficient. They had a great network of roads that connected all the cities in the empire. And they had a single currency which made trade much easier. The Mediterranean was the center of their trade network and it was very easy to get around and do business.
The provinces of the Roman Empire were trading huge volumes of commodities to one another via sea routes by the 1st century. This allowed for the movement of goods and people between the provinces and increased the prosperity of the empire as a whole.
Did ancient Rome trade with other countries?
In order to satisfy the needs of its wealthy citizens, Rome established and extended trade routes to the East. Every year, ships laden with Mediterranean commodities would sail to the ports of India and China, bringing back exotic luxuries, such as cinnamon, ivory, pepper, and silk. These trade routes allowed Rome to obtain the resources it needed to maintain its power and influence, and also helped to spread Roman culture throughout the world.
Rome’s location on the Italian peninsula, and the Tiber River, provided access to trade routes on the Mediterranean Sea. As a result, trade was an important part of life in ancient Rome. Roman merchants traded a variety of goods, including wine, olive oil, spices, and other luxury items. Trade also played a role in the Roman economy, as merchants often used their profits to purchase goods and services from other parts of the empire.
Why were sea routes better for trading
Sea routes were faster and easier to travel, and there were fewer transactions and officials involved. A trader who purchased goods in the East could have control over the goods until they reached ports in the West, and could make greater profits by eliminating middlemen.
In order to increase the income from maritime trade, the Romans built a huge number of transport ships and coastal ports such as: Civitavecchia, Ostia, Portus, Leptis Magna and Caesarea Maritima. By doing so, they were able to transport more goods and trade with more merchants, which ultimately led to more revenue.
Final Words
The ancient Romans traveled by sea and land for trading. They used ships to travel by sea and roads to travel by land.
The ancient Romans traveled for trading by sea and land. They used ships to travel between countries and to transport goods. They also used carts and horses to travel within the country.