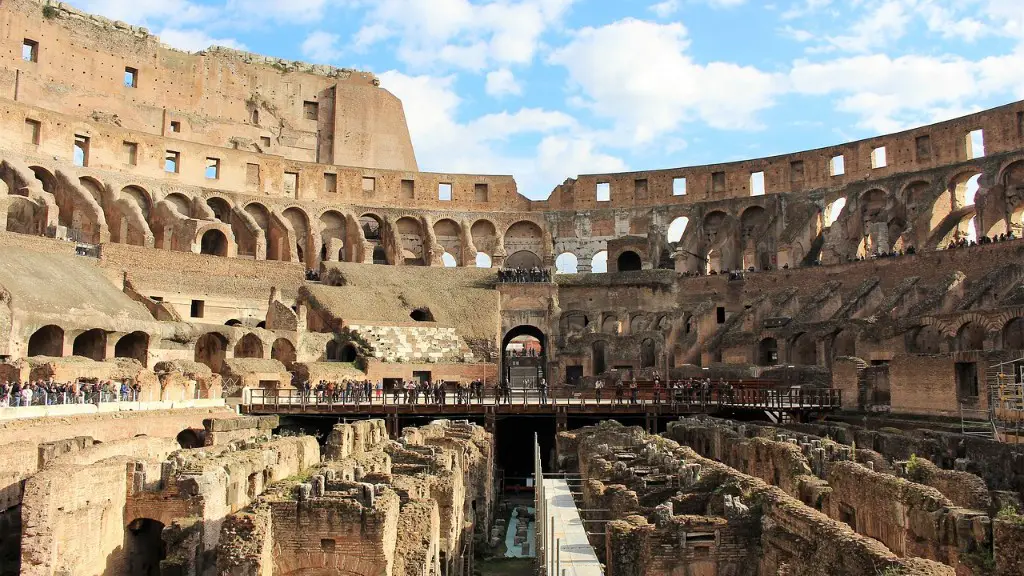
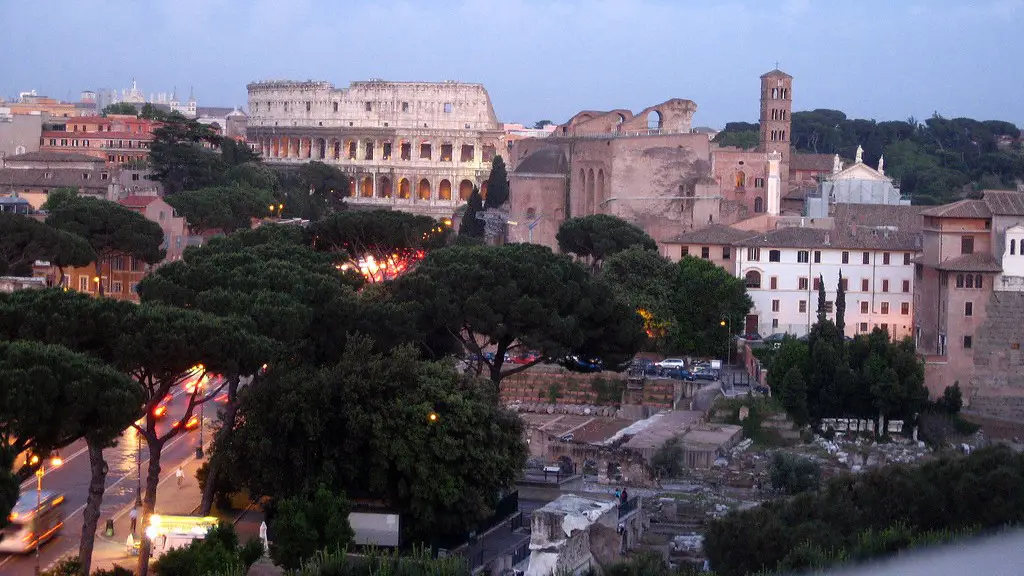
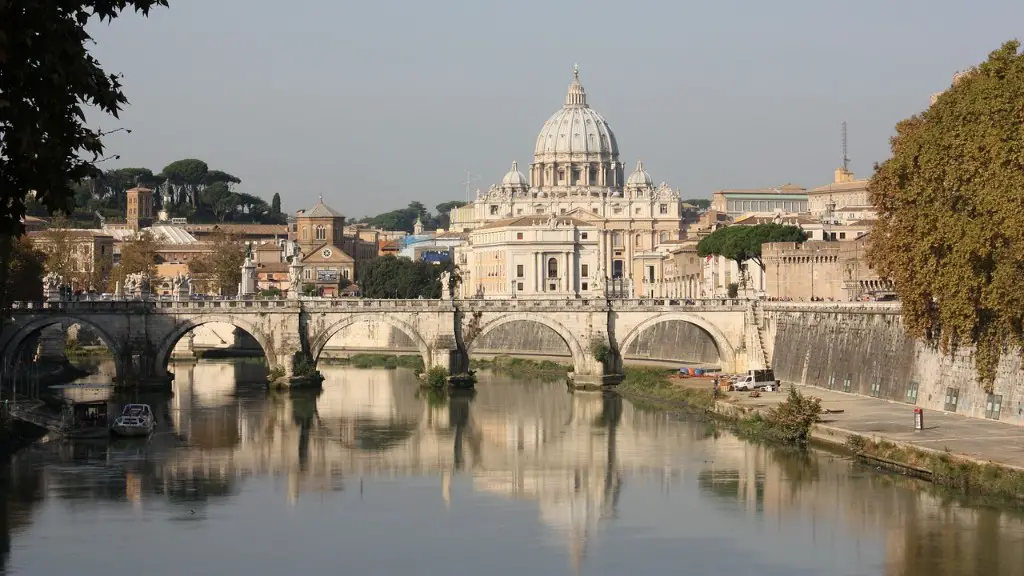
The ancient Romans are famous for their engineering accomplishments. One of the things they are most well known for is their aqueducts. The aqueducts were a system of channels and bridges that were used to transport fresh water from the mountains to the cities.
The ancient Romans built aqueducts to get fresh water from the mountains to their cities.
Where did the Roman Empire get water from?
Aqueducts are a significant part of Roman engineering and architecture. These man-made channels carried water from springs, rivers, and reservoirs into Rome’s metropolitan area. The introduction of aqueducts to the Roman water system, starting with Aqua Appia in 312 BCE, allowed water from further outside the city to be utilized and thus increased the amount of water at the Romans’ disposal. Aqueducts not only supplied Roman cities with much needed water for drinking, bathing, and sanitation, but also supported the city’s many fountains and public baths. The engineering and construction of aqueducts was a complex and impressive feat, and the aqueducts remain one of the most impressive aspects of Roman civilization.
The aqueducts were one of the most impressive achievements of the Roman engineering. To achieve a consistent, shallow slope to move the water in a continuous flow, the Romans lay underground pipes and constructed siphons throughout the landscape. The aqueducts not only supplied the cities with water for public baths and fountains, but also for private homes.
How did ancient Romans drink water
Fountains were an important part of ancient Roman life, as they provided the only source of potable water. These fountains were often ornately designed and served as a gathering place for the community. While modern Rome has many public fountains, ancient Rome only had a few, making them all the more important to the people who lived there.
The Trevi Fountain is one of the oldest water sources in Rome. The fountain dates back to ancient Roman times, since the construction of the Aqua Virgo Aqueduct in 19 BC that provided water to the Roman baths and the fountains of central Rome. The Trevi Fountain is a great example of Roman engineering and is a beautiful sight to see. If you’re ever in Rome, be sure to check it out!
Who brought water to Rome?
Appius Claudius built the first aqueduct for the city of Rome in 312 BC. This effectively created a siphon, which allowed the Romans to access clean water from outside the city. This was a major breakthrough for the Romans, who up until this point had to rely on the Tiber river for their water supply.
The Roman Empire had a complex system of sewers that were covered by stones. This was similar to the modern sewer system. The waste flushed from the latrines flowed through a central channel into the main sewage system. This system then flowed into a nearby river or stream.
Can water flow uphill naturally?
The starting point of all rivers is higher than their end point However, under the right conditions, small amounts of water can be drawn upwards, against the tug of gravity, through a phenomenon known as “capillary action” For this to occur, however, the water must be confined into a small flow space.
Aqueducts are man-made channels that are used to transport water from one place to another. They are often used to transport water from a freshwater source to a population center. Aqueducts are usually built with stone, concrete, or brick and they can be either above ground or underground. The most famous aqueducts were built by the Romans and they are still in use today.
How did Romans keep pools clean
The Roman baths were not very clean by today’s standards. They did not have disinfectants and it is likely that the bathing pools were only periodically emptied and cleaned. In addition, the baths often had built-in toilets which recycled bath water to carry away the waste. This probably meant that the water was not very clean.
People in ancient times used a variety of methods to find water that was safe to drink. They would look for water that was flowing, as this was typically cleaner than water that was stagnant. They would also look for groundwater, as this was often more protected from contamination.
Did Romans boil drinking water?
There are a few methods that the Greeks and Romans used in order to improve the quality of water if it did not satisfy their quality requirements. Some of these methods include using settling tanks, sieves, filters, and boiling water. We know this from written sources and archaeological excavations. These methods were used during antiquity and helped to improve the quality of water for the Greeks and Romans.
Rome’s tap water is some of the best in the world, with 97% of it coming from springs. The water is clean and has a great taste, thanks to the aqueducts that transport it to the city. If you’re ever in Rome, make sure to try the tap water!
Did ancient Rome have sewage
The ancient Roman sewers were designed to carry away surface water, rather than human waste. This meant that public areas of the city were served well, but crowded residential areas received little to no hygienic relief. As a result, it is important to note that the ancient Romans had a very different approach to sanitation than we do today.
Rome has a long and impressive history when it comes to water engineering. From the early days when the Tiber river was first harnessed, to the construction of the aqueducts, Rome has always been at the forefront of water technology. Having consistent access to clean water through public baths and fountains allowed Rome to keep its population healthier and happier.
What did the Romans do for toilets?
Roman latrines were not very different from the Greek latrines that came before them. They were lined with stone or wooden bench seats that had round holes in them. The holes were placed over a sewer. There was a narrower slit in the front of the hole that was in the shape of a keyhole.
It is important to have access to hygiene facilities for the poor in order to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Unfortunately, many rural areas do not have adequate facilities for the poor to use. This can lead to a number of health problems, including illness and disease.
Did the Romans have garbage
The Roman Empire was one of the most advanced civilizations of its time, and their management of waste reflected this. Most waste ended up being dumped into the River Tiber, although it is also certain that Romans had their own landfill sites, or rubbish piles, which were known as middens. The largest of these, Monte Testaccio, can still be seen today. While not perfect, the Romans had a surprisingly sophisticated system for dealing with their waste.
The Edmonston Pumping Plant is an amazing feat of engineering. It can raise water an incredible 1,926 feet – the highest single lift in the world. The plant is located at the south end of the San Joaquin Valley at the Tehachapi Mountains.
Final Words
The ancient Romans used a system of aqueducts to bring fresh water into the city. The aqueducts were a series of channels and bridges that carried water from sources outside the city to a central reservoir. From there, the water was distributed to homes and public baths.
The ancient Romans built aqueducts to bring fresh water from springs and rivers into their cities.