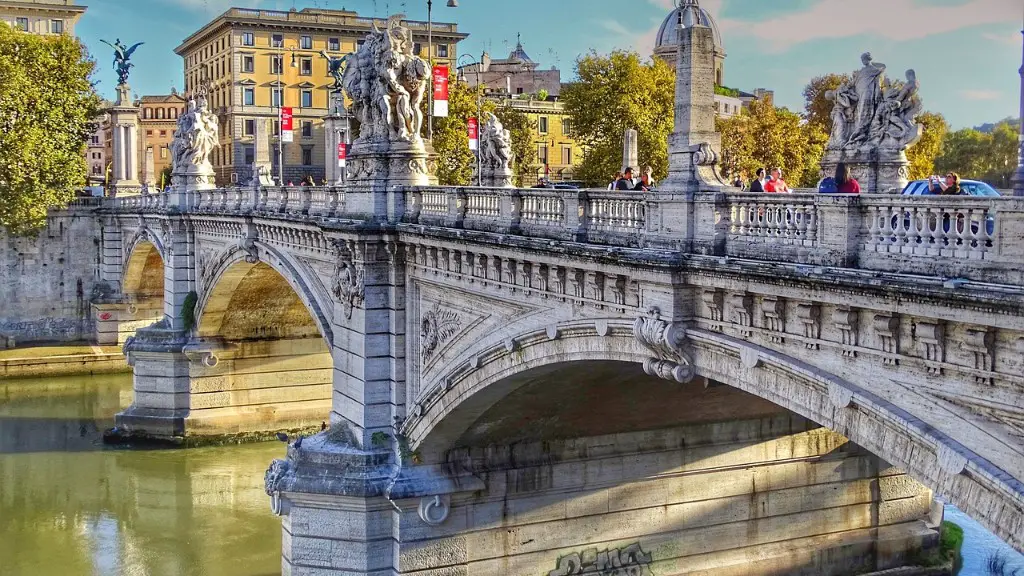
The Italian peninsula has been a crossroads of civilizations since prehistoric times. This geography–along with the peninsula’s rugged, mountains and coasts–helped shape the lives of ancient Romans.
The Italian peninsula is a boot-shaped landmass that juts into the Mediterranean Sea. Early peoples settled here because of its mild climate and access to the sea. The peninsula was also a crossroads of trade routes. This connectivity helped the Roman civilization to thrive.
The Roman Empire was one of the largest empires in history. It stretched from Britain to North Africa and from Spain to the Middle East. The empire was so vast and diverse that it was impossible to have one homogeneous culture. Instead, the Roman Empire was a melting pot of cultures.
The Roman way of life was shaped by the geography of the Italian peninsula. The mild climate and access to the sea made it possible for the Romans to grow crops and trade with other cultures. The rugged mountains and coasts also made it possible for the Romans to defend their empire.
The ancient Romans were a people who were greatly influenced by their geography. The Italian peninsula, where they lived, was very mountainous and had few good harbors. This made it hard for the Romans to travel and trade with other peoples. The Romans also had to deal with frequent earthquakes and volcanoes. These natural disasters often destroyed their crops and homes.
What 3 geographic features helped the ancient Romans the most?
Rome’s location in the center of the Italian peninsula made it a hub for trade and commerce. The city’s diverse population also made it a cosmopolitan center of culture and learning. These factors helped Rome to grow and ultimately dominate the known world.
The Alps and Apennines were two mountain ranges that served as natural barriers for Rome. The Alps provided a roadblock that forced invaders to move through narrow passages, which gave the Romans time to prepare and attack. The Apennines were also a strategic location during war time, as they provided cover and protection for the Roman army.
How did geography affect the Romans
The Roman Empire was able to grow a diverse selection of crops due to the fertile soil in the Po and Tiber River Valleys. This allowed the empire to have a food surplus to feed its population and trade with other societies. The empire also used the resulting wealth to expand its military strength.
The rich volcanic soil in the Po and Tiber River valleys makes it ideally suited for agriculture. The volcanic ash made the soil near Rome some of the best in all of Europe. New settlers arrived due to Rome’s agricultural potential. The Roman population grew quickly, with overproduction of grains, olives, and other cash crops.
What impact did geography have on the history of Rome quizlet?
Rome’s geography was a big factor in its origins and expansion. The Tiber river allowed access to the Mediterranean, but it was far enough inland that it protected Rome from invasions. The peninsula of Italy allowed trade and transportation to be easy, which helped Rome grow.
Rome’s location offered several advantages, one of which was the protection of the hills and mountains found in the peninsula. Two major groups of mountains found in Italy were very important on the development of ancient Rome. The first group was the Apennines, which served as a natural barrier between Rome and the barbarian tribes to the north. The second group was the Alps, which provided Rome with a natural border against invasions from the east.
What are 3 facts about Roman geography?
The Alps ran along the northern border and protected Rome during the winter months. The Apennines cut the Italian peninsula in half, providing Rome with natural defenses against attacks, especially in the early days when Rome was growing and developing its army. Additionally, Rome’s central location in the Mediterranean region made it a prime target for trade and commerce, which helped to further its development into a powerful empire.
Rome was famously founded on seven hills, as it was thought that this would bring good luck and protection from harm. Palatine Hill was the most prominent of these hills, as it was the highest and most centrally located. This made it an ideal spot for a fortification, as it would be easy to defend and provide a good vantage point for attacking. The island in the Tiber also made it easier to cross the river, making it a strategic location for trade and transportation.
What was the geography like in the Roman Empire
The capital city of the Roman Empire, Rome, was located in modern-day Italy. However, the Roman Empire’s Geography stretched all the way from England to Egypt, and in between: the Mediterranean basin. Different areas of the Roman Empire, eg Europe, Northern Africa, and Western Asia, were ruled by different emperors.
Rome was originally built on the banks of the River Tiber and encircled by seven hills – Aventine, Palatine, Capitoline, Caelian, Esquiline, Quirinal and Viminal. The city was then expanded over time to include the other hills of Rome – the Pincian, Janiculum, Aventine and Viminal. Rome is now divided into 14 different administrative areas, each with its own unique history and character.
What are 3 fields to which the Romans contributed?
A people known for their military, political, and social institutions, the ancient Romans conquered vast amounts of land in Europe and northern Africa, built roads and aqueducts, and spread Latin, their language, far and wide. They were a people of great achievement, and their legacy is still very evident in the world today.
Rome became a powerful state in the world by the first century BCE by being militarily powerful, politically flexible, economically prosperous, and lucky.
What are 3 Roman architectural features
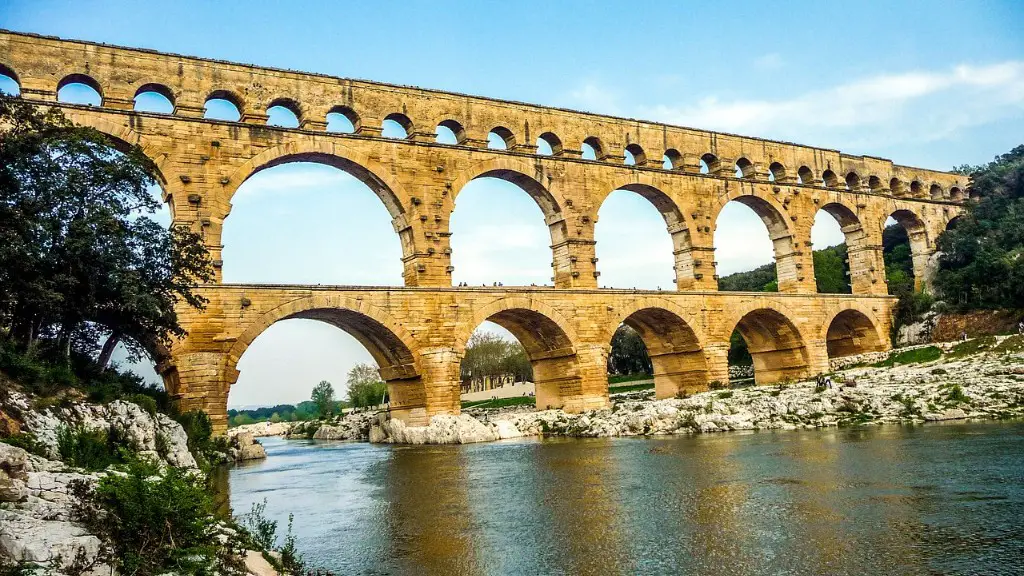
Roman architecture is characterized by its arches, domes, and columns. The Pont du Gard Aqueduct, for example, features triple-tier arches to support the structure. The Pantheon in Rome is a temple dedicated to the Roman pantheon of gods, and it features a massive dome. The Temple of Portunus in Rome also features columns, but in the Ionic style.
Rome was founded on Palatine Hill by a group of exiled Trojan prince. The Trojan prince, Romulus, decided to build a great city on the hill. Rome quickly became a rich and powerful city. The seven hills of Rome were known as the Seven Kings of Rome. The seven hills of Rome were:
1. Palatine Hill
2. Aventine Hill
3. Capitoline Hill
4. Quirinal Hill
5. Caelian Hill
6. Viminal Hill
7. Esquiline Hill
How did ancient Romans adapt to their environment?
The ancient Romans were masters of engineering and construction. They built aqueducts that carried clean water hundreds of miles to population centers where it was distributed to the homes and businesses of those who could afford it. The aqueducts were an amazing feat of engineering and allowed the Romans to enjoy a level of hygiene and cleanliness that was unmatched in the ancient world.
The influence of the Greeks on Roman culture was vast and far-reaching. Nearly every aspect of Roman culture was impacted by the Greeks, from art and architecture to philosophy and literature. The Roman empire itself was even a direct result of the Greek influence, as the Romans inherited the concepts of democracy and republic from the Greeks. As such, it is no surprise that the Greco-Roman culture was one of the most significant sources of later European civilization.
Final Words
The ancient Romans were a people who were highly influenced by their geographical surroundings. The Mediterranean Sea was a key factor in the rise of Rome as a major power. The sea allowed for easy trade and transportation, which led to the growth of the Roman Empire. Rome was also blessed with good farmland, which helped to feed the growing population. The city of Rome was situated near several major rivers, which provided a means of transportation and communication. The mountains also played a role in the development of Rome, as they served as natural barriers against invaders.
The ancient Romans were a people who were greatly influenced by their geography. They were a people who lived in a land that was abundant in resources and had a climate that was conducive to agriculture. They also had access to a vast network of trade routes that allowed them to trade with other cultures. All of these factors allowed the ancient Romans to develop into a powerful and prosperous civilization.