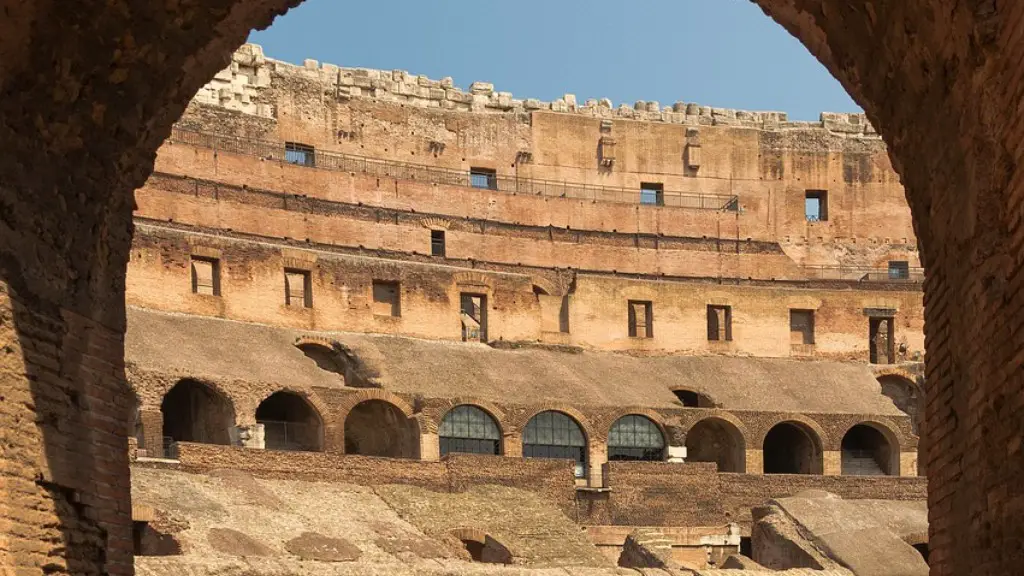
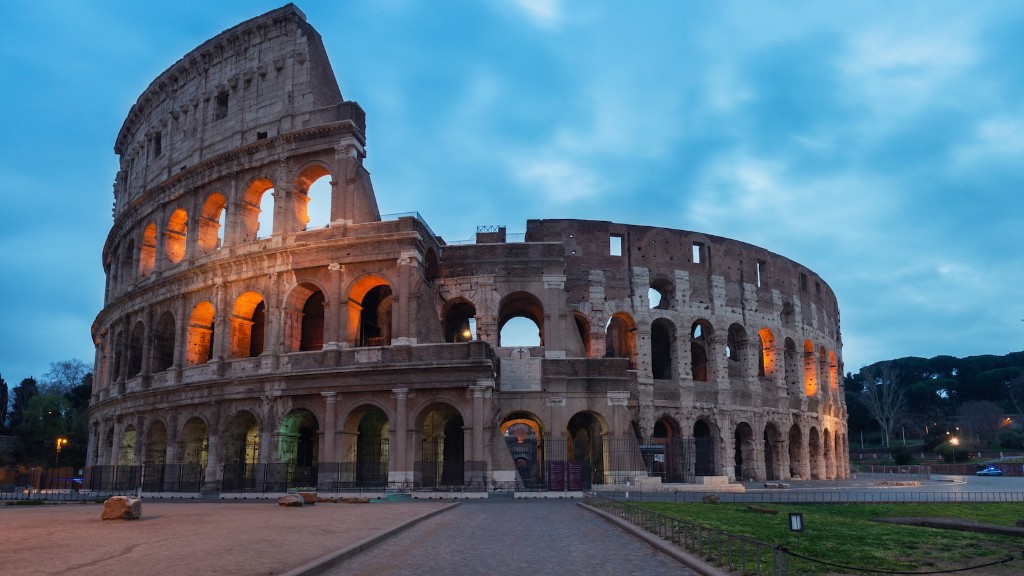
The Roman Republic was founded in 509 BCE after the city of Rome was sacked by the Gauls. The Roman Republic lasted until the end of the Roman Empire in 476 CE. The Roman Republic was a republic governed by elected officials. The Roman Empire was an autocratic state ruled by a single ruler, the emperor. The Roman Empire’, ‘The Roman Republic lasted until the end of the Roman Empire in 476 CE. The Roman Republic was a republic governed by elected officials. The Roman Empire was an autocratic state ruled by a single ruler, the emperor.
Roman society changed over time as the empire expanded and became more diverse. The early republic was dominated by the patrician class, while the plebeians (commoners) slowly gained more rights and power. Wealth also became more evenly distributed as trade and commerce increased. Slavery was an integral part of Roman society, with slave-owners having power over their slaves’ lives. This began to change in the 1st century, when slavery began to be seen as cruel and inhuman, and laws were passed to protect slaves’ rights.
What were the biggest changes under the Romans?
The Romans were a huge part of Britain’s history and development. They gave the country new towns, plants, animals, a new religion and ways of reading and counting. Even the word ‘Britain’ came from the Romans. Britain had no proper roads before the Romans – there were just muddy tracks. So the Romans built new roads all across the landscape – over 16,000km (10,000 miles) in fact! This had a huge impact on the way people were able to travel and trade, and helped to make Britain a more developed and prosperous country.
The Roman Empire did not fall, did not decline, it just transformed but so did the Germanic populations which invaded it. The Roman Empire was a complex and powerful empire that was able to adapt to change and survive. The Germanic people who invaded it were also able to adapt and change, which is why the Roman Empire was able to transform into something new.
Was ancient Rome advanced for its time
The Roman Empire was one of the most technologically advanced civilizations of antiquity. They had some of the more advanced concepts and inventions. However, many of these were forgotten during the turbulent eras of Late Antiquity and the early Middle Ages.
The Roman Republic was a period of time in which Rome was governed by elected officials. However, power gradually shifted away from the representatives and towards a centralized imperial authority. This eventually led to Rome becoming an empire, with the emperor holding the most power.
What caused the Roman Empire to change over time?
Government corruption, political dispute, and power struggle all weakened the empire. The continuous death and replacement of the emperor caused haphazard leading, with a continuous conflict between the Emperor and the Senate. The Senate was often corrupt and incompetent, leading to a power struggle that weakened the empire.
The Roman Empire was one of the most powerful empires in the world for centuries. However, there are a number of reasons why it ultimately fell. Political instability, economic and social problems, and a weakening of the frontier all contributed to the Empire’s decline.
Political instability was a big issue for the Roman Empire. There were constantly power struggles between different rulers and factions. This made it difficult for the Empire to function properly.
Economic and social problems also plagued the Empire. The rich got richer and the poor got poorer. This led to social unrest and eventually to the fall of the Empire.
Finally, the weakening of the frontier was another factor in the Empire’s decline. The frontier was the line of defense against invasions. As it weakened, the Empire became more vulnerable to attack.
All of these factors combined to contribute to the fall of the Roman Empire.
What are 7 reasons why Rome fell?
There are many reasons why the Roman Empire fell, including invasions by barbarian tribes, economic troubles and overreliance on slave labor, the rise of the Eastern Empire, and overexpansion and military overspending. Government corruption and political instability were also major contributing factors.
The fall of the Roman Empire is often attributed to the invasion of Germanic barbarian tribes. These groups swept through the empire, looting and destroying everything in their path. Eventually, they carved out areas in which to settle down, and the once-great empire was no more.
What years was Rome the strongest
Rome reached its greatest territorial expanse during the reign of Trajan (AD 98–117). However, a period of increasing trouble and decline began with the reign of Commodus (177–192).
The fall of Rome was slow and painful, lasting over a period of two and a half centuries. The ancient city of Rome, according to tradition, was founded in 753 BCE. It wasn’t until 509 BCE, however, that the Roman Republic was founded.
What advances did ancient Rome have that we have today?
Cement, the Aqueduct, Sanitation, Roads, Social care and welfare, Julian Calendar, Elements of surgery, Elements of the modern legal system
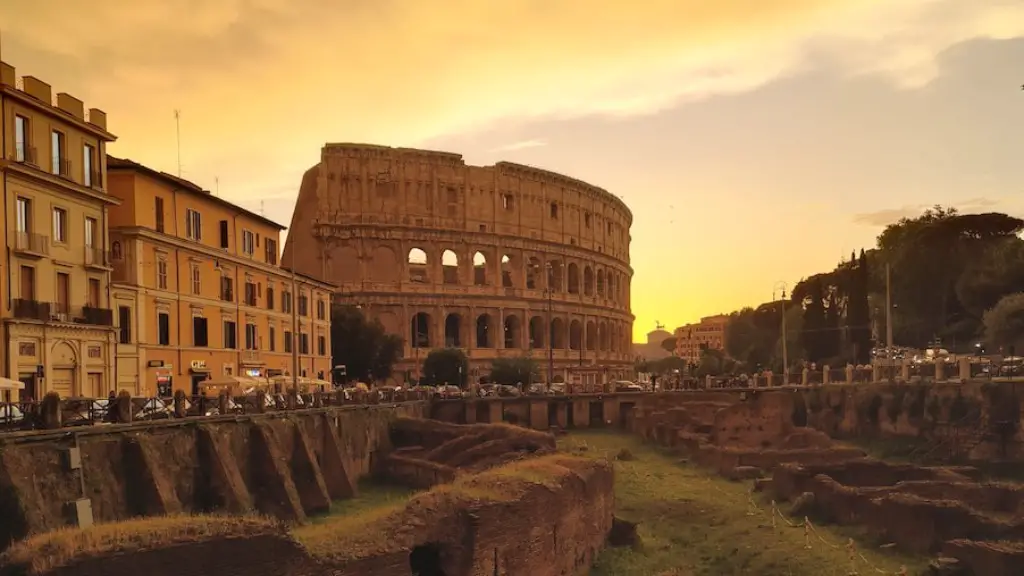
The fall of Rome was a severe blow to the West. The city of Rome was sacked by the Visigoths in 410, and the last Roman emperor of the West, Romulus Augustulus, was deposed by the German chieftain Odoacer in 476. This left the West without a major power center and vulnerable to further invasions.
What changed when Rome fell
The fall of Rome led to a significant change in political structure and culture in Europe. With the establishment of different barbarian tribes, small communities became independent from one another. Although these groups had their own kingdoms, they often shared a similar culture and lifestyle.
The most immediate effect of Rome’s fall was the breakdown of commerce and trade. The miles of Roman roads were no longer maintained and the grand movement of goods that was coordinated and managed by the Romans fell apart. This led to a decrease in the standard of living for many people as goods became more difficult to obtain. Additionally, the loss of Roman law and order made travel and trade more dangerous.
How did Rome become so powerful?
The main reason for Rome’s power was their ability to assimilate other cultures and city-states. This not only increased the taxes that funded their strong army, but also led to the development of many architectural masterpieces. This made Rome one of the greatest empires of ancient times.
1) The British Empire was the largest empire the world has ever seen. The British Empire covered 1301 million square miles of land – more than 22% of the earth’s landmass. The empire had 458 million people in 1938 — more than 20% of the world’s population.
2) The British Empire was the most powerful empire in the world for more than 150 years. The British had control of the seas, the largest army, and the most advanced economy.
3) The British Empire was started by a group of adventurers and entrepreneurs who were looking to make their fortune. The British quickly took control of North America, India, and Africa. The British Empire reached its peak in the early 20th century.
4) The British Empire was a force for good in the world. The British brought democracy, the rule of law, and modern medicine to many parts of the world.
5) The British Empire also had a dark side. The British were responsible for the slave trade, the colonization of indigenous peoples, and the exploitation of natural resources.
6) The British Empire came to an end in the mid-20th century. The British people voted to leave the empire in a series of referendums. The
Conclusion
Ancient Rome changed over time due to a variety of factors. The city of Rome itself changed, as did the people who lived there. The political system changed, as did the economy. And, of course, the culture changed over time as well.
Yes, Ancient Rome changed over time. The Roman Republic was replaced by the Roman Empire and the city of Rome was sacked by the Visigoths. The Roman Empire was then divided in two and the Western Roman Empire fell to the Lombards.